- Light weight, advantageous when constructing long power lines
- Cost up to 6 times cheaper than copper, helping optimize investment costs for large-scale projects
- Natural aluminum oxide layer prevents corrosion, protecting the conductor core
We will evaluate in detail the advantages of aluminum conductors, suggest common types of overhead aluminum conductors, and answer questions about why copper is not prioritized for this application.

1. Weight advantages
When designing an overhead power transmission line, the weight of the conductor not only affects the wire itself but also determines the entire supporting pole system and foundation.
This is the first and most important reason why aluminum wire has become the top choice for overhead power transmission systems.
Direct comparison of specific gravity:
| Material | Specific gravity (g/cm³) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | ≈ 2.7 g/cm³ |
| Copper | ≈ 8.9 g/cm³ |
So in comparison, the specific gravity of aluminum is only 1/3.3 times as heavy as copper. What's noteworthy is that although aluminum conductors need a larger cross-sectional area to achieve the same transmission capacity as copper, the total weight of aluminum wire is still significantly lighter. Specifically, with the same electrical conductivity, aluminum wire will be nearly 50% lighter than equivalent copper wire.
Technical and economic benefits from light weight:
- Reduced infrastructure construction costs: Reduces weight load on supporting poles, thereby reducing infrastructure construction costs compared to using copper wire.
- Increased span between poles: Allows greater distances between poles, reducing the cost of electrical poles.
- Safe construction: Light weight makes the process of cable pulling, wire connection, and maintenance simpler, reducing the risk of workplace accidents.
2. Price advantages
Besides weight advantages, price is the key factor where aluminum gains an advantage in large-scale power transmission projects. The price difference between aluminum and copper significantly affects the total investment cost of the power grid.
Let's review the raw material prices of copper and aluminum for an overall comparison (according to London Metal Exchange 2024):
| Material | Price/kg (USD) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | $2.2 – $2.6 |
| Copper | $8.9 – $11.0 |
Multiplier effect in large projects:
From the price table above, we can see that copper wire costs 4 times more than aluminum wire. When scaled up to national projects such as building rural power grids or industrial zones, the savings from using aluminum wire instead of copper wire become enormous.
Supply stability:
Aluminum has more abundant and stable reserves than copper, helping to better control price fluctuations in long-term projects.
Due to these economic efficiencies, not only in Vietnam, but even developed countries like the USA, Canada, and European countries all prioritize using aluminum for overhead power transmission and distribution systems.
3. Advantages of self-protective aluminum oxide layer
One of the superior characteristics of aluminum that is rarely known is its ability to self-protect against corrosive environments. This creates a significant competitive advantage compared to many other electrical conducting materials, especially in long-term outdoor applications.
3.1. Natural self-protection mechanism
When exposed to air, the aluminum surface will quickly form a very thin, hard, and insulating aluminum oxide layer (Al₂O₃). This process occurs automatically within the first few minutes when aluminum comes into contact with oxygen.
Characteristics of the aluminum oxide layer:
- Thickness: Only about 2-3 nanometers, very thin
- Properties: Extremely hard and durable, with hardness nearly equal to diamond
- Protective capability: Completely prevents the corrosion process
3.2. Benefits in practical applications
The aluminum oxide layer in practice provides many important benefits such as:
- Protecting the inner aluminum core: This oxide layer acts like a natural “armor coating,” protecting the inner aluminum core from further corrosion despite exposure to harsh environments such as acid rain, marine air, or industrial smoke.
- Superior lifespan: Thanks to this self-protection mechanism, aluminum wire can operate stably for 20-30 years.
- Environmental corrosion resistance: Suitable for use in coastal environments with high salinity, industrial areas, or places with many corrosive chemicals.
4. Some types of aluminum cables used overhead
Based on the three core advantages of aluminum, the electrical power industry has developed many types of aluminum cables for overhead applications. Among the most commonly encountered are aluminum conductor steel reinforced (ACSR) and aerial bundled cable (ABC), each optimized for different environments.
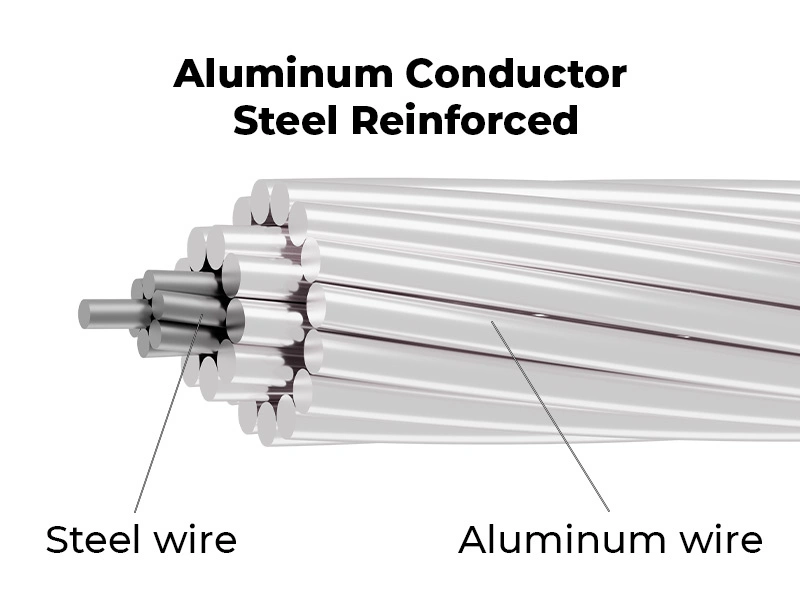
4.1. Aluminum conductor steel reinforced (ACSR)
Structure and technical characteristics:
- Structure consists of 2 main parts: a steel core for mechanical strength and an aluminum layer wrapped outside with the function of electrical conduction. If used in coastal environments or corrosive conditions, the wire will be coated with an additional neutral grease layer.
- High mechanical tension (33-284 kN)
Main applications: Commonly used in areas with harsh terrain or environmental conditions such as rivers, mountains, seas…
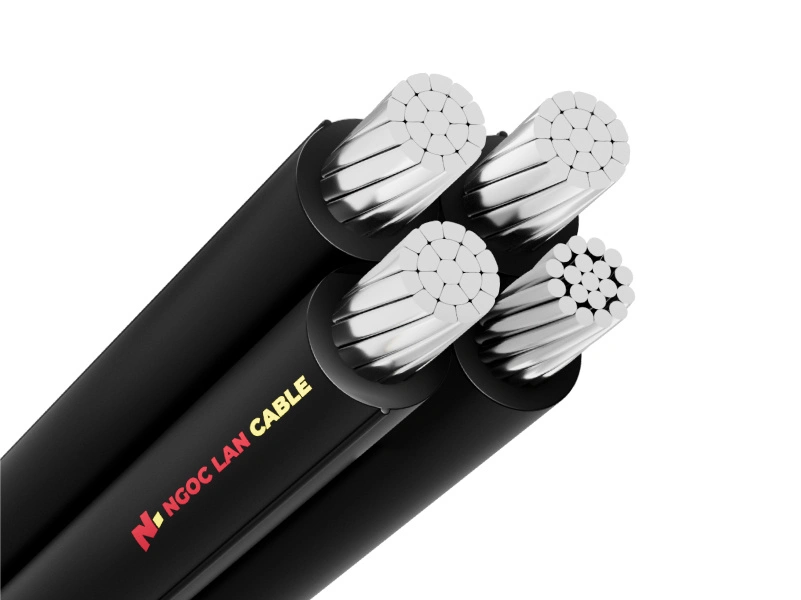
4.2. Aerial bundled cable (ABC)
Structure and technical characteristics:
- Cable structure can have 2-4 aluminum cores with XLPE insulation, twisted together
- Nominal voltage (Uo/U): 0.6/1kV
- Lightning impulse test voltage 1.2/50µs:
- Nominal conductor area < 35mm²: 15kV.
- Nominal conductor area ≥ 35mm²: 20kV.
- Maximum nominal operating temperature of conductor: 90ºC.
- Maximum short circuit temperature in 5s of conductor: 250ºC.
Main applications: Overhead power distribution in urban areas, residential areas, industrial zones, factories…

At Ngoc Lan Cable, we manufacture both types of products according to TCVN and international standards, fully meeting the needs from large transmission projects to small-scale distribution systems.
However, through the process of consulting and supporting customers, we have noticed there are still some common questions about conductor material selection and electrical safety. We have compiled the most frequently asked questions from engineers, contractors, investors and provided answers about the advantages and disadvantages of each material type, helping you better understand the appropriate application context for each solution.
5. Related questions about overhead aluminum conductors
5.1. What percentage (%) of electrical conductivity does aluminum wire have compared to copper wire?
Aluminum wire has electrical conductivity equal to approximately 61% – 63% compared to copper wire when measured on the same cross-sectional area. To transmit the same electrical current, aluminum wire needs a cross-sectional area approximately 1.5 – 1.6 times larger than copper wire.
5.2. Are all overhead aluminum wires bare conductors?
No. There are two commonly encountered types:
- Bare aluminum conductors or aluminum conductor steel reinforced: No insulation sheath, used for transmission lines passing through sparsely populated areas, hills and mountains, where large safety clearances and good heat dissipation are required.
- Aluminum cables with sheath: Have safe insulation layers, used for distribution power grids in urban areas and residential areas to ensure safety and aesthetics.
5.3. Should aluminum cable be used for indoor electrical systems?
Not recommended. Although theoretically possible, aluminum wire is not suitable for indoor electrical wiring for the following reasons:
- Complex connections: Requires higher connection techniques to ensure safety, not compatible with outlets and switches designed for copper wire.
- Less flexible: Aluminum wire is stiffer and more prone to breaking when bent repeatedly in tight spaces.
- Large cross-section: Requires wire with larger cross-sectional area than copper wire to handle the same load, causing difficulties when running wire through conduits.
Therefore, copper wire remains the preferred choice for safety and efficiency in indoor electrical systems.
6. Conclusion
Through this article, we have somewhat understood the reason why do overhead power lines use aluminum? Aluminum wire has proven to be the most economically and technically efficient choice for overhead power transmission lines thanks to 3 core advantages:
- Light weight
- cost than copper
- Good corrosion resistance thanks to aluminum oxide layer
At Ngoc Lan Cable, we provide complete aluminum wire and cable solutions from ACSR to ABC, meeting TCVN and international standards. Contact us immediately for free consultation on your project and receive the most competitive quotes in the market.
 VN
VN