Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
1. Overview of low voltage cables
1.1 What is a low voltage cable?
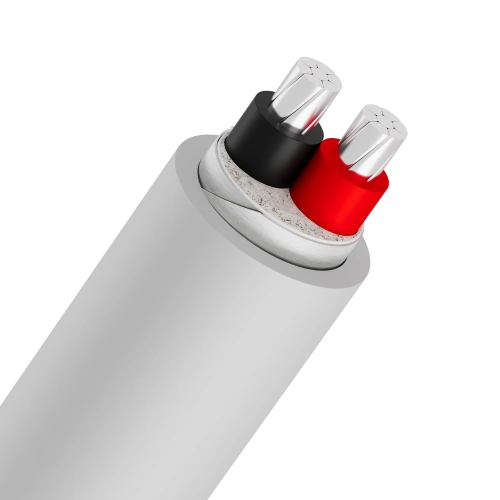
Low voltage cables are specially designed cables for power transmission and distribution at rated voltages of 0.6/1kV and below. These are crucial components in electrical systems, connecting distribution transformers to end-user equipment in homes, businesses, and other facilities.1.2 Structure of low voltage cables
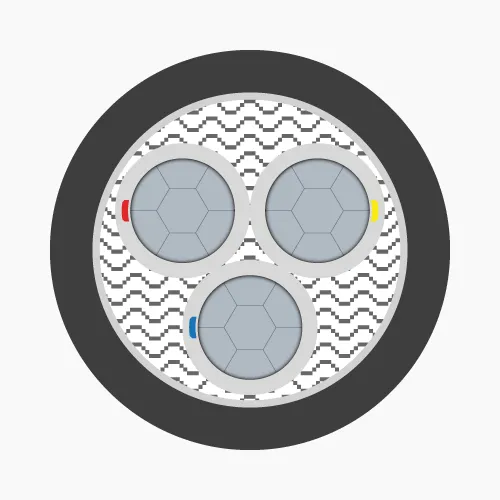
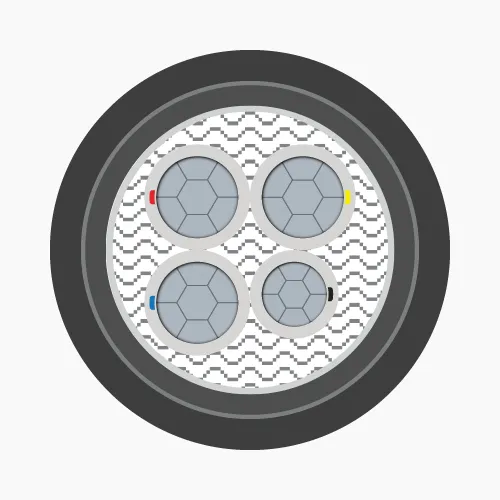
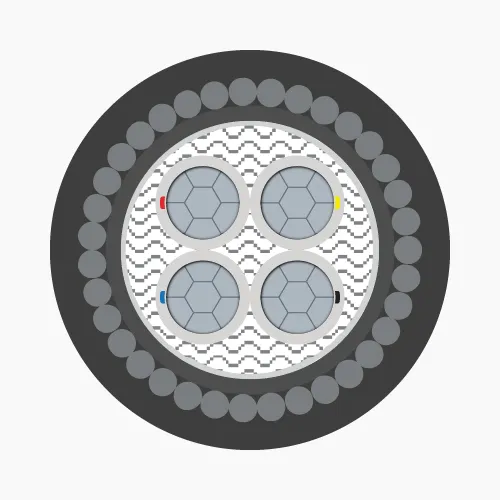
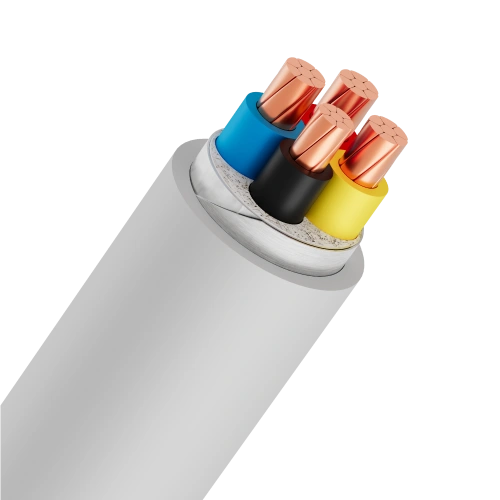
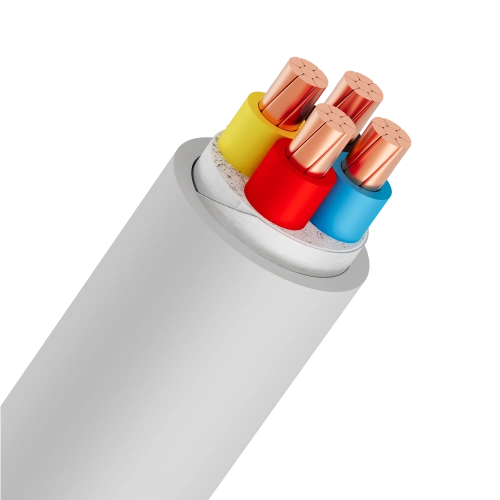
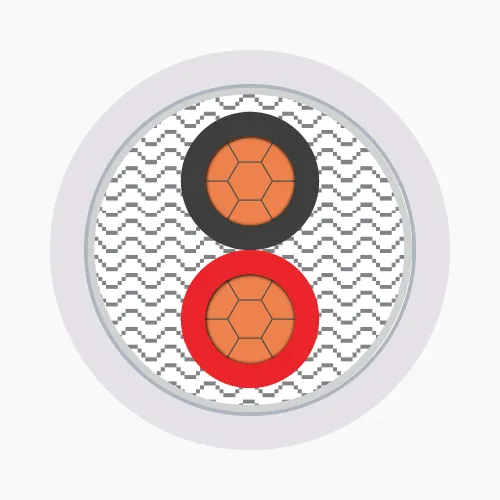
Low voltage cables consist of three main layers, each serving a specific function:-
- Conductor: Made from copper or aluminum, available in solid, stranded, or compressed circular forms, primarily for conducting electricity
- Insulation: Typically XLPE or PVC material, functions to prevent electrical contact between conductors and protect the core
- Outer sheath: PVC coating that protects the cable from external environmental factors

1.3 Technical characteristics and standards
Production standards and technical characteristics are strictly followedTechnical standards:
-
- Vietnamese standards: TCVN 5935-1; TCVN 6612; TCVN 6610, TCVN 5933… (Ngoc Lan Cable is applying these standards to cables such as AV, AVV, CVV, CXV, CVV/DSTA, CXV/DATA...)
- International standards: IEC 60502-1; IEC 60228; IEC 60227... (Ngoc Lan Cable is applying these standards to cables such as AV, AXV, CV, CXV, CXV/SWA, AXV/SWA, AVV/SWA ...)
-
- Rated voltage: 300/500V, 450/750V or 0.6/1kV
- Voltage test 50Hz - 5min: 2kV (300/500V), 2.5kV (450/750V), 3.5kV (0.6/1kV)
- Max. conductor temperature in normal operation: 70°C (PVC) or 90°C (XLPE).
- Max. conductor temperature in short-circuit for 5s max duration: 160°C (PVC) or 250°C (XLPE).
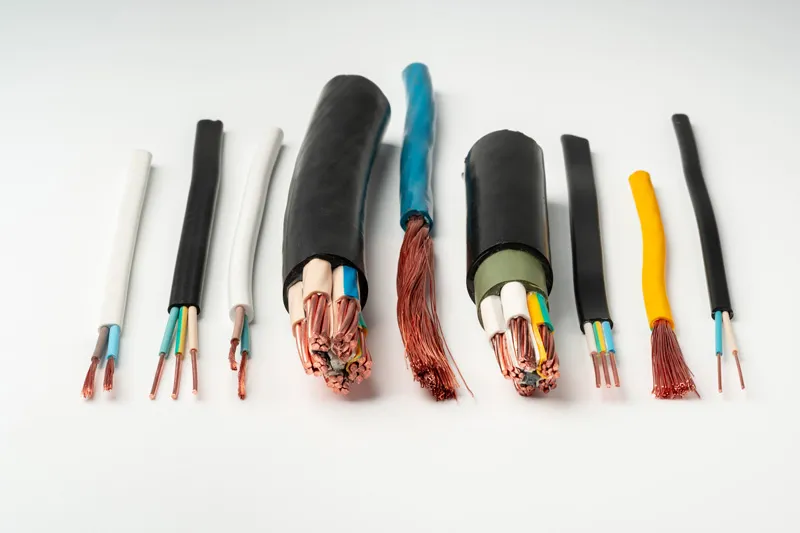
2. Types of low voltage cables
Classification of low voltage cables is typically based on voltage rating, conductor material, number of cores, insulation material, and application:2.1 Classification by voltage rating
-
- Rated voltage 300/500V - 450/750V: These voltage ratings are commonly used in residential applications for low power transmission needs such as lighting fixtures and household appliances.
- Rated voltage 0.6/1kV: This voltage rating is used in industrial and construction projects such as factories, manufacturing plants, and infrastructure projects.
2.2 Classification by conductor material
-
- Copper conductors: Made from pure copper (~99.99%), offering high electrical conductivity, efficient transmission, low energy loss, and high durability.
- Aluminum conductors: More cost-effective than copper but with lower conductivity. Commonly used in applications where high conductivity is not critical.
2.3 Classification by number of cores
-
- Single core: One conducting core with PVC or XLPE insulation
- 2-cores: Two conductors, identified by red and black insulation colors (PVC) or marking tapes (XLPE).
- 3-cores: Three conductors, marked by red, yellow, blue insulation (PVC) or color tapes (XLPE).
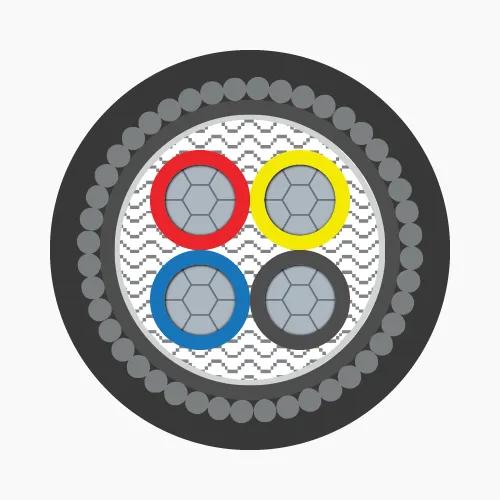
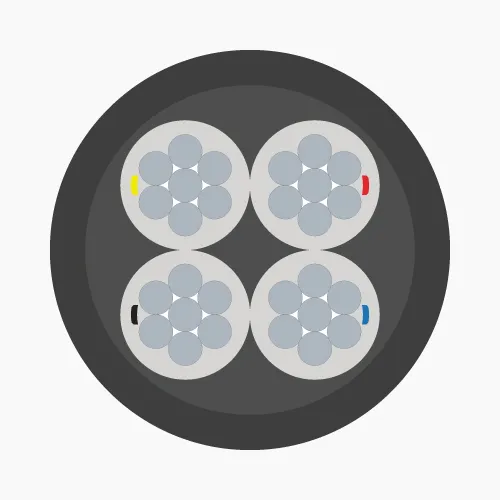
- 4-cores: Four conductors, identified by red, yellow, blue, black insulation (PVC) or marking tapes (XLPE).
- 3 phase + 1 neutral: Three phase conductors plus one neutral conductor, marked accordingly.
2.4 Classification by insulation material
-
- XLPE insulation: Superior heat resistance (90ºC), high durability, preferred for demanding environments.
- PVC insulation: Common, cost-effective material with lower heat resistance (70ºC), suitable for standard applications.
3. Applications of low voltage cables
Low voltage cables find wide application across various sectors:-
- Residential power distribution in apartments, buildings, and homes, connecting main power sources to electrical devices like lighting, fans, air conditioners, refrigerators, washing machines, TVs, and computers.
- Industrial machinery operation, production lines, and lighting systems in factories and manufacturing facilities.
- Traffic signal systems, street lighting, and automated toll stations, using moisture-resistant and weatherproof cable varieties.
- Automation control systems, specifically designed for industrial equipment and machinery control signal transmission. Control cables with various core configurations ensure accurate, stable, and safe signal transmission in harsh industrial environments.
- Traditional communication systems, though fiber optic cables have largely replaced them due to superior bandwidth and transmission speed capabilities.

4. Guidelines for selecting low voltage power cables
When choosing low voltage power cables, you need to consider the following factors:Rated current
This is the maximum current that the power cable can safely and continuously withstand over a long period of time. If the current exceeds the rated value, the cable will be overloaded, generating a large amount of heat, which may damage or ignite the cable. The rated current also depends on environmental conditions (ambient temperature, soil, installation depth). Therefore, you must choose a cable with an appropriate conductor cross-section and installation conditions.
Voltage drop
Voltage drop is the loss of electrical energy during transmission. The voltage drop must not exceed 2.5% of the rated voltage (e.g., 5.5V for 220V single phase, 9.5V for 380V three phase). Voltage drop depends on the current, cable length, power factor and cable resistance. If the voltage drop is too large, a cable with a larger cross-section should be selected.
Cable resistance parameter
The resistance parameter of the power cable determines the conductivity and safety of the electrical wire system. Therefore, you need to pay special attention to this parameter. When choosing low-voltage power cables, it is advisable to choose cables with low resistance parameters.
Conductor cross section
The cross-section of the electrical conductor determines the electrical load and system safety. For home electrical systems, choose a small cross-section suitable for the usage needs. For systems with many devices and large electrical loads, prioritize choosing the largest possible cross-section. For residential low-voltage power cables, the minimum cross-section must be 0.5 mm² to ensure user safety.
Cable weight
In addition to the cross-section of the power cable, its weight also indicates the quality of the product. Since the core of the power cable is made of copper and coated with many protective layers, standard power cables are quite heavy. For lightweight power cables, it is difficult to ensure quality and the core is easily replaced with inferior materials. Therefore, research the weight standards of low-voltage power cables before purchasing the product.
Choosing a reputable manufacturer
It is necessary to choose manufacturers with prestige in the market, who have achieved quality certifications such as ISO or QUACERT, meeting domestic and international standards such as TCVN, IEC... to ensure quality and safety during construction and use.
 VN
VN