Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Low Voltage Cables
Service entrance cables, also known as SE cables or Muller cables, are essential components in electrical metering and power supply systems. With excellent conductivity, high durability, safety features, and versatile applications, SE cables stand out from regular electrical wires. When choosing the right service entrance cable for your needs, it's crucial to consider factors such as intended use, power consumption, conductor material, and insulation type.
 In practice, SE cables are widely used in residential homes, office buildings, factories, and industrial facilities. Selecting the appropriate type of Muller cable based on power consumption and installation conditions helps ensure stable operation of the electrical system.
In practice, SE cables are widely used in residential homes, office buildings, factories, and industrial facilities. Selecting the appropriate type of Muller cable based on power consumption and installation conditions helps ensure stable operation of the electrical system.
 Depending on specific industry requirements, additional layers may be included in the cable structure, such as color tapes (for core/phase identification) or inner sheaths for cable rounding.
Although SE cables have a higher upfront cost, their long-term economic benefits outweigh regular wires due to their reliability and longevity.
Depending on specific industry requirements, additional layers may be included in the cable structure, such as color tapes (for core/phase identification) or inner sheaths for cable rounding.
Although SE cables have a higher upfront cost, their long-term economic benefits outweigh regular wires due to their reliability and longevity.

1. What is a Service Entrance Cable (Muller Cable)?
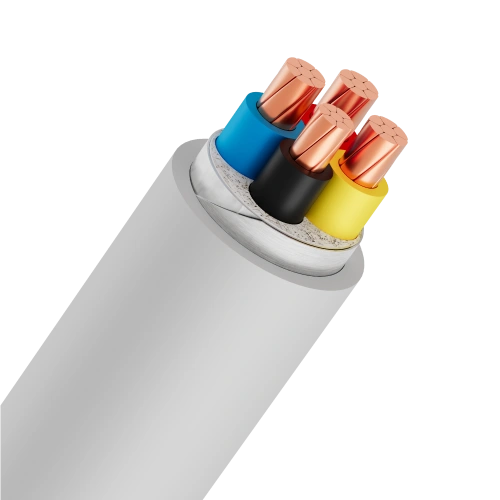
Service entrance cables, often referred to as "Muller cables", have the product codes DK-CVV, DK-CXV, or DK-AVV. These cables play a vital role in connecting electric meters to the power grid, ensuring efficient transmission and distribution of electricity. Unlike ordinary electrical wires, SE cables are specially designed to deliver high performance and safety in metering and supply applications. Typically, service entrance cables consist of copper or aluminum conductors insulated with PVC or XLPE materials. This construction provides excellent durability and safety during operation.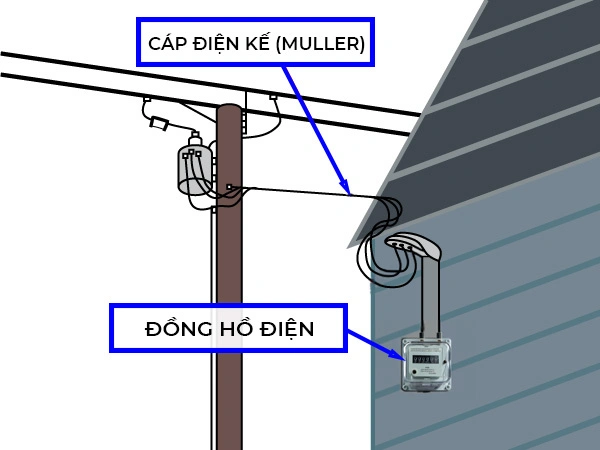 In practice, SE cables are widely used in residential homes, office buildings, factories, and industrial facilities. Selecting the appropriate type of Muller cable based on power consumption and installation conditions helps ensure stable operation of the electrical system.
In practice, SE cables are widely used in residential homes, office buildings, factories, and industrial facilities. Selecting the appropriate type of Muller cable based on power consumption and installation conditions helps ensure stable operation of the electrical system.
2. Common Types of Service Entrance Cables
Service entrance cables can be classified based on several criteria:- Conductor Material:
- Copper core SE cables (DK-CVV or DK-CXV): Utilize pure copper conductors for high and stable conductivity.
- Aluminum core SE cables (DK-AVV): Utilize aluminum alloy conductors, which are lighter and more affordable compared to copper cables.
- Number of Cores:
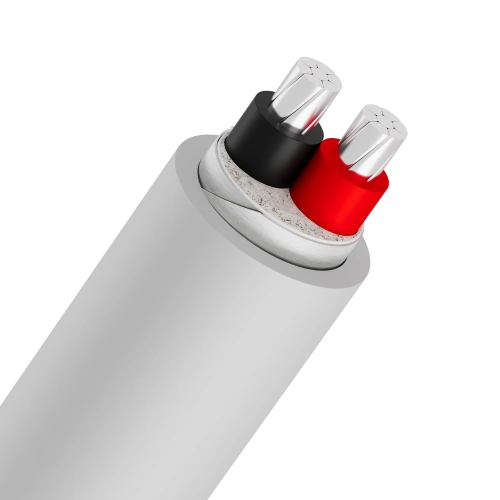
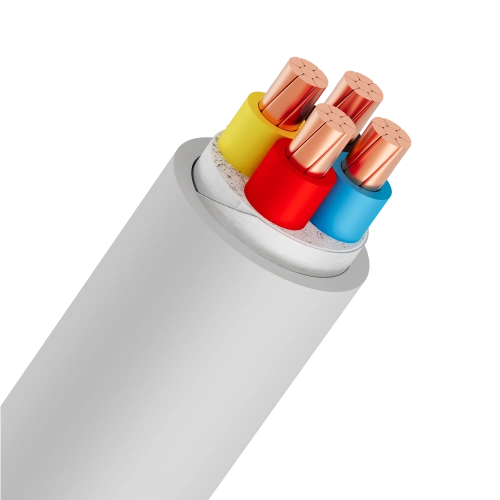
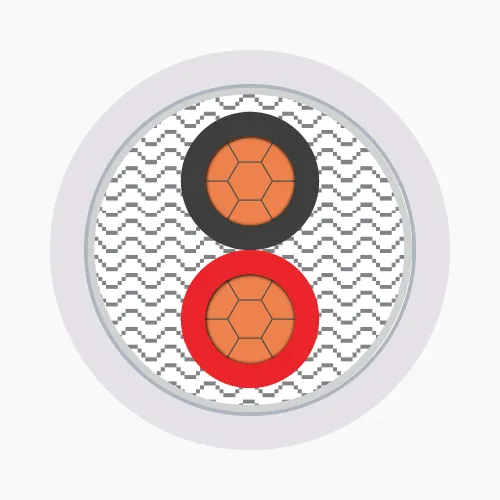
- 2-core cables: Common type, often used for single-phase lines.
- 3-core cables: Consist of 2 phase cores and 1 neutral/ground core.
- 4-core cables: Consist of 3 phase cores and 1 neutral/ground core.
- Insulation Material:
- PVC insulation: PVC plastic insulation layer provides moisture resistance and can withstand operating temperatures around 70°C.
- XLPE insulation: Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulation layer tolerates higher temperatures, around 90°C.
3. Structure of Service Entrance Cable Layers
A service entrance cable typically consists of five layers of materials:- Conductors: Made of copper or aluminum, including soft strands (class 2) twisted concentrically or compressed tightly.
- Insulation: Using PVC or XLPE plastic materials.
- Filler layer: PP or PVC fillers to increase durability and aesthetics.
- Metallic shield: Aluminum tape to prevent electricity theft.
- Outer sheath: Made of PVC plastic to protect the inner layers from environmental impacts.
 Depending on specific industry requirements, additional layers may be included in the cable structure, such as color tapes (for core/phase identification) or inner sheaths for cable rounding.
Depending on specific industry requirements, additional layers may be included in the cable structure, such as color tapes (for core/phase identification) or inner sheaths for cable rounding.
4. Key Advantages of Service Entrance Cables
Service entrance cables offer several superior benefits compared to regular electrical wires:- Excellent conductivity: With pure copper or aluminum conductors, SE cables ensure efficient and stable power transmission, minimizing energy losses.
- High durability: The insulation and outer sheath layers of SE cables can withstand environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and UV radiation, extending the service life.
- Safety: With excellent insulation properties and impact resistance, SE cables reduce the risk of electrical leakage, ensuring user and equipment safety.
- Versatile applications: Service entrance cables can be used in various environments and projects, from residential to industrial, meeting diverse metering and power supply needs.
5. How to Select the Right Service Entrance Cable
To choose an appropriate service entrance cable, consider the following factors:- Determine the intended use:
- Cables for residential homes or apartments: Typically use cables with smaller cross-sections and lower power ratings.
- Cables for factories or large projects: Require cables with larger cross-sections and higher power ratings.
- Calculate power consumption:
- Base the cable cross-section on the maximum power consumption of the electrical system and refer to the technical specifications table.
- Calculate power consumption reserve to ensure stable cable operation even with minor load changes.
- Select conductor and insulation materials:
- Copper cables are suitable for applications requiring high and stable conductivity.
- Aluminum cables are appropriate for cost-saving purposes.
- PVC or XLPE insulation layers depend on the working environment conditions.
6. Safe Installation and Usage of Service Entrance Cables
To ensure safety and efficiency when using service entrance cables, adhere to the following principles:- Hire a reputable installation company: Installing SE cables requires professional knowledge and skills. Choose an experienced and reputable installer to ensure quality and safety.
- Comply with electrical safety regulations: During installation and operation, strictly follow electrical safety rules, such as using protective equipment, disconnecting power when not in use, and not attempting repairs without proper training.
- Perform regular inspections and maintenance: Conduct periodic inspections and maintenance of SE cables to promptly detect and address any damage, ensuring the electrical system remains in optimal condition.
7. Frequently Asked Questions
- Can service entrance cables be used outdoors?
- SE cables can withstand harsh weather conditions such as sun, rain, and wind. However, to ensure long-term safety and stability when installing outdoors, protective measures should be taken to shield the cables from direct environmental impacts, such as using cable conduits or specialized junction boxes.
- How to determine the appropriate cable cross-section?
- To select the correct cable cross-section, refer to the maximum power consumption of the electrical system and the technical specifications table. Additionally, calculate power consumption reserve to ensure stable cable operation even with minor load changes.
- Should aluminum cables be used instead of copper cables?
- Aluminum cables have the advantages of being lighter and more affordable compared to copper cables. However, copper cables have better conductivity and higher durability. For short installation projects, copper cables are recommended, while aluminum cables are more suitable for longer distances and larger cross-sections. Ultimately, the choice of cable type depends on the specific project requirements and investment budget.

 VN
VN