Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium Voltage Cables
1. Introduction to medium voltage power cables
1.1. Concept
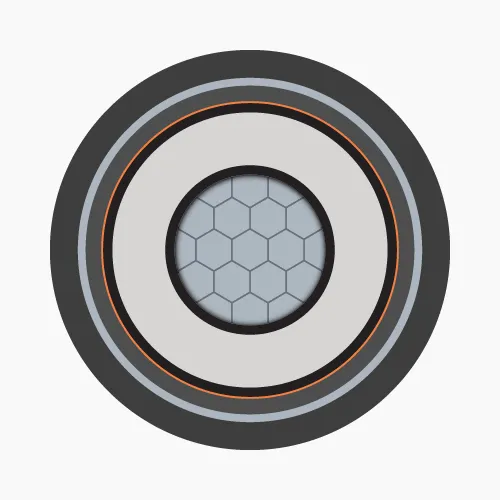
Medium voltage power cables are electrical cables used to transmit power at voltage levels from 1kV to 35kV. They are critical components in the power distribution system, connecting high voltage grids to main substations and distribution substations. From there, the voltage is stepped down to supply residential and industrial consumers.1.2. Construction
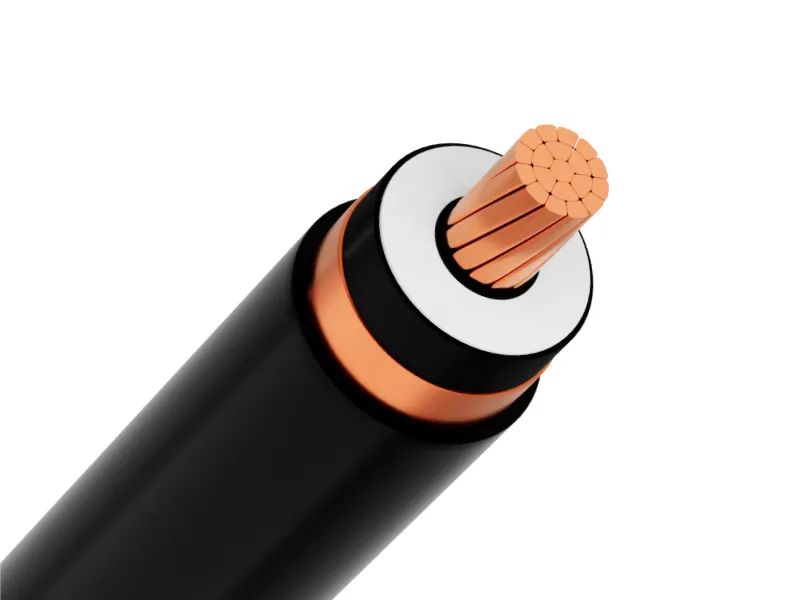
Medium voltage power cables consist of the following main components:-
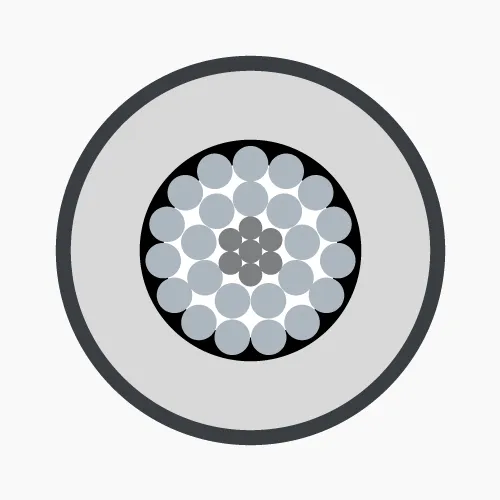
- Conductor: Made of copper or aluminum, the conductor is concentric stranded or compact round.
- Conductor screen: Made of extruded semiconductive compound (Ethylene Copolymer Carbon Black) or semiconductive tapes to maintain uniform electric field and limit insulation breakdown.
- Insulation: XLPE insulation prevents current leakage and ensures safety.
- Insulation screen: Made of semiconductive compound or tape covering the insulation layer. The electric field generated by the current flow remains inside the cable, provided that the semiconductive layer surface is grounded.
- Metallic screen: Usually a soft copper tape wrapped around the insulation. Its main function is to reduce electromagnetic interference for more stable transmission.
- Outer sheath: Made of HDPE or PVC, protecting the entire cable structure from environmental impacts.

1.3. Technical specifications and applicable standards
Medium voltage power cables have much more complex constructions than low voltage cables and are often used in critical projects. Therefore, strict national and international standards are always applied, such as:-
- Vietnam Standards: TCVN 5935-2, TCVN 5935-1, TCVN 6612, TCVN 5064... (currently applied by Ngoc Lan Cable for MV cables like ACXHe, CXHe, CXV/S, AXV/S, ACXV...).
- International Standards: IEC 60502-2; IEC 60228... (currently applied by Ngoc Lan Cable for MV cables like AXHe, ACXe, AXV/AWA, CXV/DSTA, CXV/SWA...).
-
- Rated voltage (Uo/U): 1.8/3(3.6)KV, 3.6/6(7.2)kV, 8.7/15 (17.5)kV, 6/10(12)KV, 12/20(24)kV.
- Voltage test 50Hz - 5min: 6.5kV [1.8/3(3.6)KV], 12.5 kV [3.6/6(7.2)kV], 30.5kV [8.7/15 (17.5)kV], 21kV [ 6/10(12)KV], 42 kV [12/20(24)kV].
- Max. conductor temperature in normal operation: 90ºC.
- Max. conductor temperature in short-circuit for 5s max duration: 250ºC.
2. Types of medium voltage power cables
2.1. Overhead medium voltage cables
This type of MV cable is used for overhead distribution systems supplying medium voltage power, with the following basic construction:-
- Conductor: Solid copper or aluminum wires concentrically stranded in multiple layers or compacted. Aluminum conductors are made like ACSR to increase tensile strength. Some types have longitudinal water blocking depending on application requirements.
- Conductor screen: Usually made of semiconductive polymer compound.
- Insulation: XLPE (cables with outer sheath will have an additional insulation screen layer).
- Sheath: Made of PVC or XLPE.
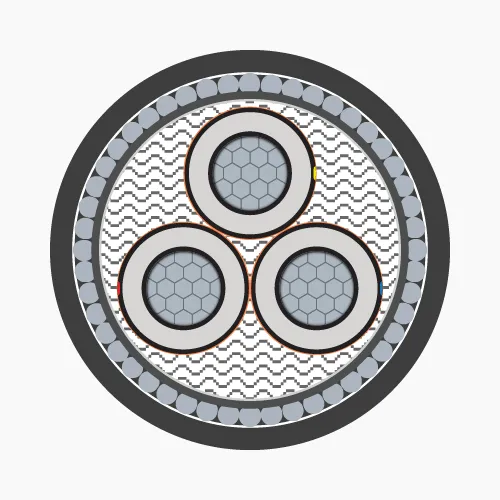
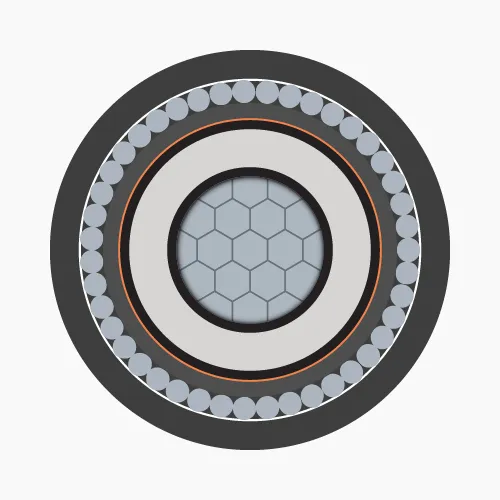
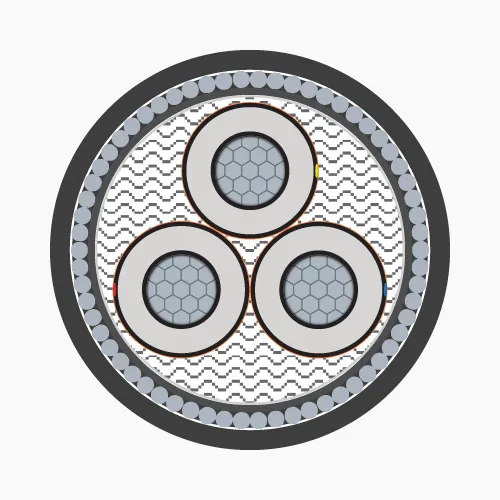
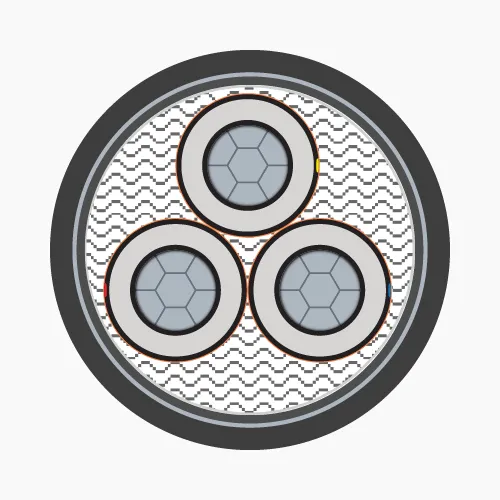
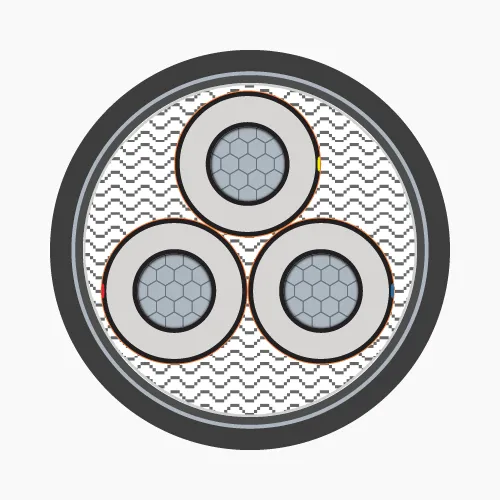
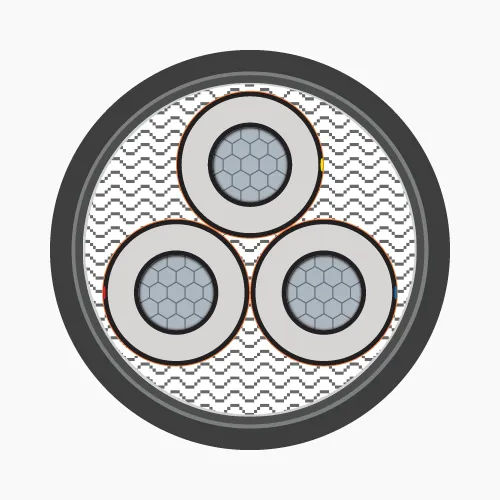
2.2. Underground medium voltage cables
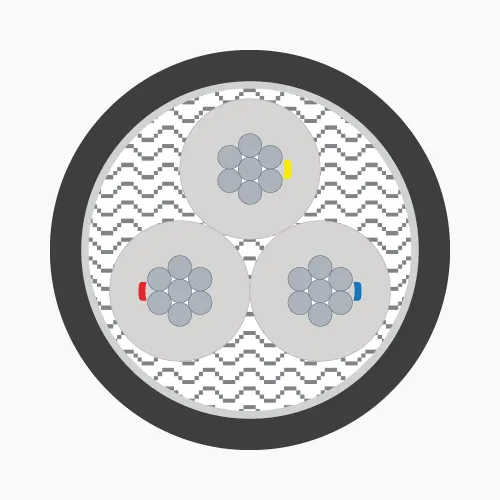
Underground medium voltage cables are typically installed underground in MV distribution systems. This special cable is only manufactured in 1-core and 3-core types.-
- Conductor: Made of annealed copper or solid aluminum wires, concentrically stranded in single or multiple layers and compacted.
- Conductor screen: Conductor is covered with a semiconductive plastic layer (Ethylene Copolymer Carbon Black) to maintain uniform electric field.
- Insulation: XLPE or EPR, HEPR.
- Insulation screen: Semiconductive plastic layer (Ethylene Copolymer Carbon Black) extruded over the insulation. The electric field generated by current flow remains inside the cable, provided that the semiconductive layer surface is grounded.
- Metallic screen: Made of copper or aluminum, can be tape, wire or combination of both, or braided wire mesh. Applied over the insulation screen and grounded to ensure zero voltage on insulation screen surface.
- Filler: Used in 3-core cables, usually made of PP (Polypropylene), PVC or synthetic fibers (Polyester) and wrapped with PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) tape.
- Separator: PVC.
- Armor protection:
- Steel tape or galvanized steel wire (for 3-core cables)
- Aluminum tape or wire (for 1-core cables)
-
- Sheath: PVC or HDPE.
3. Applications of medium voltage power cables
Knowing the applications of medium voltage power cables will make it easier for you to choose the right type of cable for each of your purposes.3.1. Applications in industry and construction
-
- Medium voltage power cables are used to transmit energy from high-voltage substations to points of use such as factories and internal power distribution systems.
- Used to supply power to power grids, for residential, commercial and industrial areas.
- Installed underground for medium voltage distribution such as in trenches, trays, cable ladders, conduits or buried directly in the ground...
3.2. Applications in renewable energy
Medium voltage power cables play an important role in solar power and wind power systems, helping to transmit energy from these natural energy sources to the main power system.4. Guidelines for selecting medium voltage power cables
Having the skills and knowledge when purchasing will help you choose the right medium voltage power cable product.Step 1: Analyze technical requirements and environment
Determine the basic parameters of voltage and current suitable for the system scale. Evaluate the installation environment conditions including temperature, humidity and special requirements for fire resistance, waterproofing, and electromagnetic interference.
Step 2: Select conductor and insulation materials
Consider between copper conductors (high conductivity, good heat resistance) and aluminum (low cost, light weight) based on requirements and budget. Choose appropriate insulation materials (PE, EPR, XLPE) according to specific operating conditions.
The insulation layer plays a decisive role in the life and efficiency of the cable. Common insulation materials such as PE, EPR or XLPE each have their own characteristics suitable for specific environments and operating conditions.
Step 3: Cable structure
The cable structure needs to be optimally designed with the appropriate number of conductors and a reliable shielding system. The metal shield not only protects the cable from mechanical impacts but also helps limit electromagnetic interference. The outer sheath needs to be selected to suit the installation environment, with the ability to withstand impacts from temperature, chemicals and other environmental factors.
Step 4: Evaluate standards and certifications
Choose products that ensure compliance with international (IEC) and domestic (TCVN) standards on safety, performance and reliability of medium voltage power cables.
Step 5: Technical-economic analysis
Cost-benefit analysis needs to be done thoroughly, including initial investment costs, operating and maintenance costs over the life of the cable. Choosing a reputable manufacturer with a good warranty policy and after-sales service will help ensure long-term investment efficiency.
5. Frequently asked questions (FAQ) about medium voltage power cables
5.1. How long is the lifespan of medium voltage power cables? What factors affect it?
Medium voltage power cables have an average lifespan of 25-30 years under normal usage conditions. However, the actual lifespan depends on many factors such as environmental factors (temperature, humidity, UV rays...), operating factors (load level, overload frequency...), maintenance quality...5.2. What should be noted when installing underground medium voltage cables?
Burial depth requirementsThe cable burial depth must comply with technical standards, suitable to the geological conditions and safety requirements of the area. In particular, medium voltage cables need to be buried deeper than low voltage cables to avoid mechanical impacts from surface activities.
Safe distances
The distance between cable routes must strictly comply with standards to prevent electrical discharge and minimize mutual influence. Proper arrangement will facilitate maintenance and repair work.
Mechanical protection measures
Underground cables need to be protected by a layer of specialized material on top, combined with high-strength conduits. At critical locations, warning signs should be installed and appropriate impact and compression protection solutions implemented.
Inspection and quality assurance process
Comprehensive cable quality inspection before installation, post-installation testing, and complete technical documentation are mandatory requirements to ensure safe system operation.
Labor safety
Workers must be fully equipped with protective gear, trained in techniques and safety procedures. Expert supervision is necessary to ensure the work is performed to standard.
6. Conclusion
In the current strong development trend of infrastructure, the role of the wire and cable manufacturing industry is becoming increasingly important, especially for high-tech products such as medium voltage cables. Therefore, mastering knowledge about the construction, technical characteristics and applications of medium voltage power cables becomes essential for electrical engineers.When properly applied with technical standards, strictly adhering to installation procedures and performing periodic maintenance, medium voltage power cables not only achieve optimal lifespan but also help optimize investment costs for projects.
 VN
VN