Detailed instructions for reading wire and cable symbols for low voltage power cables, medium voltage power cables, including conductor materials, insulation, core structure, and rated voltage according to IEC and TCVN standards, together with Ngoc Lan Cable.
Understanding the symbols on electric wires correctly not only helps you choose suitable products for low voltage and medium voltage power cables but also ensures safety during use. This article will decode in detail the symbols on electric wires from conducting materials, insulation to core structure and rated voltage, helping you read and understand technical specifications in a professional manner.
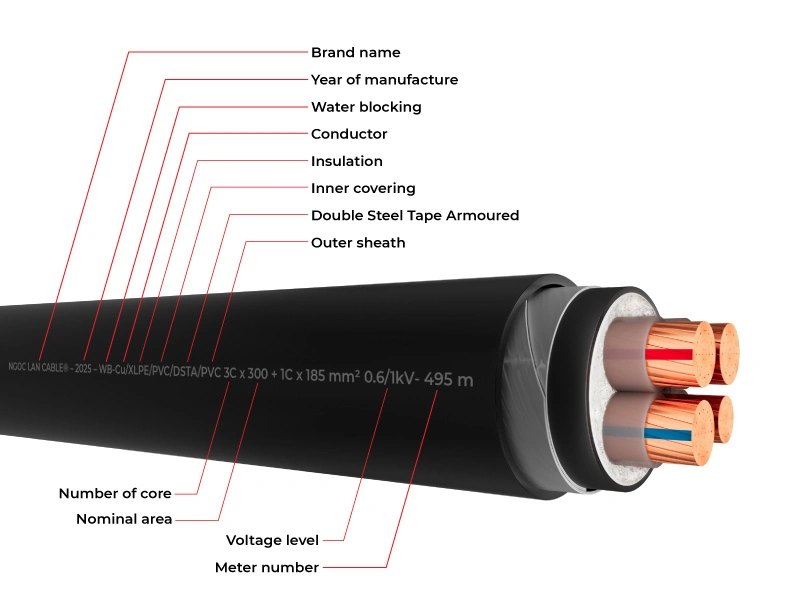
1. Why do you need to clearly understand electric wire technical specifications?
Do you know that according to statistics from the Police Department of Fire Prevention, Fighting and Rescue (PCCC and CNCH) in the first 6 months of 2024, 72.9% of fires were related to electrical systems and equipment, in which the selection and installation of components such as electric wires, sockets, or unsuitable protective devices could be a contributing factor to the incidents? This emphasizes the importance of clearly understanding the technical criteria when building a safe electrical system. Let's explore with Ngoc Lan Cable the following three important reasons to protect your project from unnecessary risks.
With many complex symbols on electric wires, a complete guide to reading electric wire symbols will help you avoid risks in the selection and use process, especially in projects with high technical requirements. Mastering how to read wire specifications will help you choose the right cable type for the project.
1.1. Preventing risks of electric shock, fire and explosion
Each type of electric wire is designed with specific characteristics to ensure safety under particular conditions of use. According to TCVN 6610-4 standard, important safety factors include:
- Permissible operating temperature: PVC-insulated wires work safely at 70°C, while XLPE wires can withstand temperatures up to 90°C
- Insulation layer thickness: From 0.6mm to 2.2mm depending on the cross-section and application
1.2. Choosing the right wire, saving costs
The selection of suitable conductors is based on the following technical factors:
- Wire cross-section: Directly affects current carrying capacity and power loss
- Conductor material: Copper (Cu) has lower resistivity than aluminum (Al), reducing losses on the line
- Manufacturing technology: Affects the quality and efficiency of conductors
1.3. Meeting electrical technical standards
According to IEC 60502 standard (applied in Vietnam through TCVN 5935), electric cables need to meet:
- Structural requirements: Suitable copper/aluminum cores and metallic screens
- Voltage withstand capability: Breakdown voltage test from 2.5kV to 36kV
- Ability to resist water penetration and withstand high temperatures according to standards
2. Decoding the symbols of conductive materials
In the design and installation of electrical systems, selecting suitable conductive materials is a critical factor in determining performance and safety. With a comprehensive guide to reading electrical wire symbols, you can easily identify different types of conductive materials through the following detailed technical specification table. Understanding the symbols on electrical wires and cables will help you accurately identify the type of material used for each cable.
When reading the specifications on electrical wires, pay attention to the following cable symbols related to conductive materials:
| Symbol | Meaning | How to read and technical characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Cu | Pure copper | – Read as “copper wire” or “copper conductor” – Conductivity: 100% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard) – Maximum operating temperature: 70°C (with PVC insulation), 90°C (with XLPE insulation) |
| Al | Aluminum | – Read as “aluminum wire” or “aluminum conductor” – Conductivity: 61% IACS – Commonly used for power transmission lines – Cost about 30% lower than copper |
| CCA | Copper Clad Aluminum | – Read as “copper clad aluminum wire” – Aluminum core covered with a layer of copper – Conductivity: 65-75% IACS depending on copper/aluminum ratio – Intermediate solution in terms of cost and performance |
| ACSR | Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced | – Read as “aluminum conductor steel reinforced” – Structure: Steel core for strength covered by conductive aluminum strands – Application: Overhead power transmission lines – High mechanical strength, can withstand large tensile forces |
3. Classification of insulation material symbols
Insulation material is an essential protective layer for electrical conductors, determining the heat resistance, mechanical durability and safety of electrical wires and cables. A detailed guide to reading electrical wire symbols must include an analysis of insulation material types according to technical standards. Understanding the cable symbols related to insulation materials is a crucial element in reading electrical wire specifications accurately.
Below is a detailed analysis of the symbols on electrical wires and cables related to insulation materials:
| Symbol | Meaning | How to read and technical characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| PVC | Polyvinyl Chloride | – How to read: Spell out each letter “P-V-C” – Maximum working temperature: 70°C – Rated voltage: 300/500V – 0.6/1kV – Insulation resistance: 0.0028-0.013 MΩ·km – Insulation thickness: 0.6-2.2mm (depending on cross-section) – Application: Residential and indoor industrial projects |
| XLPE | Cross-linked Polyethylene | – How to read: Spell out each letter “X-L-P-E” – Maximum working temperature: 90°C – Rated voltage: 0.6/1kV – 35kV – 1.5 times better overload capacity than PVC – High mechanical strength: Resistant to tensile and bending forces – Application: Industrial, substations, power systems |
| LSFH | Low Smoke Free Halogen | – How to read: Spell out each letter “L-S-F-H” – Smoke generated during combustion: < 50% compared to PVC – Halogen-free: Safe during combustion – Exhaust gas pH: > 4.3 (less corrosive) – Limiting oxygen index (LOI): > 30% – Application: High-rise buildings, hospitals, schools |
Each type of insulation material has its own advantages in specific applications:
- PVC is suitable for common electrical systems thanks to its reasonable cost
- XLPE is chosen for systems requiring high thermal stability
- LSFH is the optimal solution for projects with strict fire safety requirements
4. Dissecting the structure of electrical wires through symbols
After learning about insulation materials, we will delve deeper into the technical structure of electrical wires. This part of the guide to reading electrical wire symbols will help you understand the characteristics and applications of each type of wire through the following symbols:
| Symbol | Meaning | How to read and technical characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 3Cx50 + 1Cx25 | Multi-core electrical wire structure | – How to read: “3 phase cores, 50mm² cross-section + 1 neutral core 25mm²” – 3 cores carry the main electric current (phase) – 1 neutral core balances the current – Application: 3-phase electrical systems, substations, industrial projects |
| 7/0.8 | Stranded wire structure | – How to read: “7 strands, 0.8mm diameter each strand” – Flexible structure, vibration resistant – High durability due to multiple wire strands – Application: Electrical motor systems, mobile machinery |
| 1×16 | Single core electrical wire | – How to read: “1 core, 16mm² cross-section” – Simple, rigid conductor – Suitable for short wire runs – Application: Fixed electrical systems, local connections |
5. Interpreting voltage and power ratings
In this comprehensive guide to reading electrical wire codes, we will delve into the crucial parameters of voltage and power ratings – key factors determining the transmission capacity of electrical wires:
| Code | Meaning | Interpretation and technical specifications |
|---|---|---|
| 300/500V | Low voltage rating | – Reading: “300 over 500 Volts” – Uo = 300V (voltage to ground) – U = 500V (voltage between phases) – Application: Residential electrical systems, lighting |
| 0.6/1kV | Medium voltage | – Reading: “0.6 over 1 kilovolt” – Uo = 0.6kV (voltage to ground) – U = 1kV (voltage between phases) – Application: Industrial electrical systems, transformer substations |
| 50Hz | Industrial frequency | – Reading: “Fifty hertz” – Standard grid frequency – Electrical oscillation cycle: 0.02 seconds – Application: Global electrical systems |
6. Protective layers and armoring
In this guide to reading electrical wire codes, we will explore the protective layers that enhance the safety and durability of electrical wires under various operating conditions:
| Code | Meaning | Interpretation and technical specifications |
|---|---|---|
| DSTA (Double Steel Tape Armoured) | Double steel tape armor | – Reading: Read each letter “D-S-T-A” – Double steel tape armor protection – Impact and penetration resistant – Application: Harsh environments, outdoor installations |
| DATA (Double Aluminum Tape Armoured) | Double aluminum tape armor | – Reading: Read each letter “D-A-T-A” – Double aluminum tape armor for interference shielding – Lightweight, corrosion-resistant – Application: Single core underground cable systems, light industrial |
| SB (Shielded Braid) | Copper shielding braid | – Reading: Read each letter “S-B” – Copper shielding braid – Electromagnetic interference shielding – Application: Medical and automotive fields |
7. Standards and certifications
A comprehensive guide to reading electrical wire codes must address international and national standards – crucial benchmarks ensuring the quality and safety of electrical wires:
| Code | Meaning | Interpretation and technical specifications |
|---|---|---|
| IEC 60502 | International standard for power cables | – Reading: “I-E-C six zero five zero two” – Specifies requirements for low and medium-voltage power cables – Includes requirements for materials, testing and safety – Globally applicable for cable manufacturers |
| TCVN 6610-4 | Vietnamese standard for electrical wires | – Reading: “Vietnamese standard six six one zero four” – Specifies requirements for electrical wires used in Vietnamese conditions – Assesses the quality and safety of electrical wires – Suitable for Vietnamese climate and environmental conditions |
8. Important considerations when reading wire specifications
Understanding the technical specifications of electrical wires correctly is crucial. Each manufacturer has its own approach and interpretation of the technical parameters, requiring users to pay close attention.
A detailed guide to reading electrical wire codes will help you avoid mistakes that could affect system safety. The most important principle is to always carefully check the specifications on product packaging and accompanying technical documents. Different manufacturers may use different codes and terminology but must comply with common standards such as IEC 60502 and TCVN 6610-4.
Some key points to note:
- Compare technical specifications between different manufacturers
- Check the suitability of the electrical wire for the usage environment
- Verify quality certifications and standards
9. Frequently asked questions about electrical wire specifications
After in-depth analyses of standards and certifications, this guide to reading electrical wire codes will answer common questions to deepen your understanding of wire specifications.
9.1. Can electrical wires with a lower rated voltage than the system voltage be used?
Answer: No! Using electrical wires with a lower rated voltage than the system is extremely dangerous. In that case:
- High risk of overload
- Can cause short circuits and fires
- Reduces lifespan of the electrical system
- Potential risk of electric shock
9.2. What is wire cross-section?
Cross-section is the area of the conductor's cross-section, playing a key role:
- Determines current carrying capacity
- Directly affects power loss
- Larger cross-section, better conductivity
Example:
- 1.5mm² wire: Suitable for power outlets
- 4mm² wire: Used for high power devices
- 10mm² wire: Industrial electrical systems
9.3. What types of electrical wires are commonly used in residential buildings?
Three main types of electrical wires:
Lighting wires
- Small cross-section: 1.5mm²
- Material: PVC
- Voltage: 300/500V
Outlet wires
- Cross-section: 2.5mm²
- Material: PVC or XLPE
- Voltage: 450/750V
Wires for high power devices
- Cross-section: 4-6mm²
- Material: XLPE
- Voltage: 0.6/1kV
10. Mastering wire specifications – Ensuring safe usage
After studying this guide to reading electrical wire codes, you have grasped how to read and understand the codes on electrical wires professionally. The following important knowledge will help make the selection and use of electrical wires safer and more efficient:
- Conductive materials: Copper (Cu), aluminum (Al), copper clad aluminum (CCA), and aluminum conductor steel reinforced (ACSR).
- Insulating materials: PVC, XLPE, LSFH – selected based on requirements for temperature, durability, and installation environment.
- Conductor structure: For example: 3Cx50 + 1Cx25.
- Rated voltage: 300/500V, 0.6/1kV.
This article not only provides a knowledge foundation for beginners but also offers in-depth information to enhance understanding in the electrical field.
If you are looking for a reliable resource or need further advice on high-quality electrical wire products, Ngoc Lan Cable is always ready to assist. We not only provide useful knowledge but also deliver safe, durable electrical wire solutions suitable for all usage needs. Please share your opinions or ask questions in the comments section – we look forward to listening and supporting you!
 VN
VN