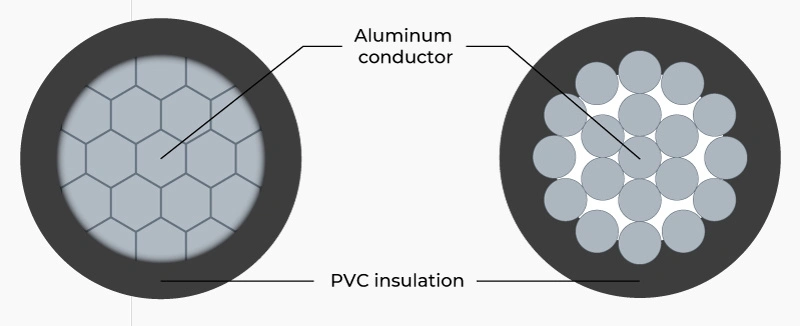
In the electrical industry, the term “AV” often causes confusion with Audio/Video in the electronics field. However, AV electrical wire is actually the designation for a specialized low-voltage power cable type featuring an aluminum conductor with PVC insulation covering, and represents one of the most common types for residential applications due to its optimal balance between cost and technical performance.
Misunderstanding this definition can lead to incorrect material selection for an entire electrical project. This article provides a comprehensive technical handbook on AV electrical cables, focusing on aspects that engineers and contractors need to understand:
- Standard definition according to TCVN national standards and IEC with detailed technical specifications
- Technical analysis of each component structure and operating principles
- In-depth comparison with copper CV cable in terms of performance and economics
- Practical applications and safety installation notes according to standards
To understand the essence of AV electrical cable, we need to start from the standard technical definition and applicable industry standards.
1. Standard definition and applicable standards for AV electrical cable
Understanding the precise definition of AV cable not only helps avoid confusion but also ensures the correct product selection for each specific application in electrical systems.
1.1 Standard technical definition
AV electrical cable is a type of low voltage power cable with aluminum conductor (Aluminum) and PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) plastic insulation. This product belongs to the group of power cables used for electrical transmission and distribution systems. The cable has a voltage rating of 0.6/1 kV, designed for fixed installation in construction projects.
The “AV” designation according to Vietnamese electrical industry convention means:
- A: Aluminum (Aluminum conductor)
- V: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride plastic insulation material)
Beyond the basic definition, understanding the applicable technical standards will help ensure product quality and safety.
1.2 Applicable technical standards
AV electrical cables are manufactured and tested according to strict standards to ensure quality and operational safety:
Vietnamese standards and equivalent international standards:
- TCVN 5935-1 equivalent to IEC 60502-1, specifying extruded insulation cables for rated voltages from 1kV to 30kV
- TCVN 6612 equivalent to IEC 60228, specifying standards for conductors of insulated cables
These standards ensure AV cables meet requirements for safety, load capacity, and service life. During consultation for large projects, Ngoc Lan Cable always strictly adheres to these standards in the manufacturing process.
1.3 Basic technical characteristics
Here are the technical characteristic parameters of AV cable:
- Rated voltage (Uo/U): 0.6/1 kV
- Voltage test 50Hz – 5min: 3.5kV
- Max. conductor temperature in normal operation: 70°C
- Max. conductor temperature in short-circuit for 5s max duration:
- Conductor cross-section > 300 mm²: 140ºC.
- Conductor cross-section ≤ 300 mm²: 160ºC
After mastering the definition, standards, and technical characteristics, understanding the detailed structure will provide better insight into the operating principles and advantages/disadvantages of AV cable.
2. Detailed structure of AV power cable
Understanding the structure of AV electrical cable not only helps in selecting the right product but also supports efficient installation and maintenance of electrical systems.
2.1 Layer-by-layer structure analysis
AV electrical cable has a simple structure but is optimized for performance and durability. The structure consists of two main components arranged from inside to outside.
Layer 1: Aluminum Conductor
The aluminum conductor is the core component that determines the cable's electrical transmission capacity.
Material and characteristics:
- Made from pure aluminum with minimum 99.5% purity
- Structure: Class 2 conductor, concentric stranded, with or without compaction
- Number of wires: Complies with TCVN 6612 standard
Layer 2: PVC Insulation
The PVC insulation layer surrounding the conductor plays an important role in ensuring safety and preventing electrical leakage.
2.2 Advantages of AV Structure
Technical aspects:
- Simple structure helps reduce manufacturing costs
- PVC insulation layer protects the conductor from mechanical impacts, provides flame retardancy (for insulation with flame retardant additives), UV resistance, etc.
- Lightweight aluminum conductor, convenient for transportation and installation
Application aspects:
- Suitable for overhead lines (low load on structures)
- Easy construction in spaces with limited access
- Low investment cost for long cable runs
This structure creates an ideal balance between technical performance and economics, making it suitable for many applications in low voltage electrical systems in Vietnam.
3. Comparison of AV electrical cable with CV
The comparison between aluminum AV cable and copper CV cable is an important consideration in electrical system design. The decision to choose which cable type directly affects the performance, cost, and durability of the entire project.
3.1 Detailed comparison table of technical characteristics
| Comparison Criteria | AV Cable | CV Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity | Only 61% compared to CV cable | 100% (simulation number for comparison) |
| Weight | Only 30% as heavy as CV cable | Heavier |
| Investment cost | Saves 30-40% compared to CV cable | Significantly higher |
| Resistivity (20°C) | 0.0283 Ω.mm²/m | 0.017241 Ω.mm²/m |
| Oxidation resistance | Lower | Better |
| Required cross-section | 1.6 times larger than CV wire for the same load current | Smaller |
3.2 Analysis of advantages and disadvantages of each type
Analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of aluminum AV cable and copper CV cable will help you make a comprehensive assessment of each type.
Advantages of AV cable:
- High economy: Reduces investment cost by 30-40% compared to copper cable, less price volatility. Particularly effective for long cable runs
- Lightweight: Reduces load on support structures, convenient for transportation and installation
- Natural corrosion resistance: Self-forming aluminum oxide layer protects the conductor
- Soft aluminum characteristics: Easy to bend, cast, and machine process
Disadvantages to note:
- Lower electrical conductivity: Requires 1.6 times larger cross-section to achieve the same load capacity
- Complex connections: Requires high technical expertise to prevent galvanic corrosion
- Low tensile strength: Requires more careful handling during construction
Advantages of CV cable:
- Good electrical conductivity: Allows use of 1.6 times smaller cross-section compared to AV cable for the same power
- Good mechanical durability: High tensile strength, withstands large mechanical stress during installation and operation
- Good corrosion resistance, long service life
Disadvantages to note:
- Investment cost 30-40% higher than AV cable, easily fluctuates according to raw material prices on the world market
- Significantly heavier weight compared to AV cable, increases load on support structures
- Low economy for long cable runs, material costs account for a large proportion
3.3 Selection recommendations by application
Choose AV cable when:
- Project has limited budget: Optimizes cost while ensuring technical safety
- Overhead lines: Light weight reduces pressure on electrical poles and structures
- Straight cable runs with few branches: Minimizes complex connection points
- Industrial electrical distribution systems: Suitable for factories and industrial zones
Choose CV cable when:
- Project requires high performance standards
- Limited installation space, requiring cables with compact cross-section
- Complex systems with many branches, requiring stable connections
- Harsh environments requiring high mechanical durability and superior corrosion resistance
From our experience consulting projects in Vietnam, we always advise customers to carefully consider the specific conditions of each project to make appropriate choices.
4. Applications and installation notes for AV electrical cable
Proper technical installation of AV electrical cable not only ensures safety but also maximizes the lifespan and performance of the electrical system.
4.1 Common applications
Industrial electrical systems:
- Overhead electrical cable installation serving outdoor electrical transmission systems
- Running in cable trays for construction projects, factories, industrial zones
- Electrical distribution systems in commercial buildings
- Power lines connecting from transformer stations to main electrical panels
Residential electrical systems:
- Power supply for residential areas, villas
- Public lighting electrical systems
- Connection of electrical equipment, power supply for residential electrical devices
4.2 Important notes when installing AV electrical cable
Note the important issues below to help you avoid incidents during installation:
- Avoid dragging cables on the ground to prevent damage to the insulation layer
- Check the condition of cable reels before construction
- Handle connections carefully, use cable lugs or electrical wire connectors (cable connectors, cable clamps) for aluminum-copper cable connections
- Comply with TCVN 9208 standard on regulations for installing cables and electrical conductors in industrial construction projects
- Completely cut off power before construction
- Use complete personal protective equipment
- Check voltage before making connections
5. Frequently asked questions about AV electrical cable
During our consultation and project implementation process, we often receive many questions from engineers and contractors about the technical characteristics and practical applications of AV cable.
5.1. Can AV wire be used for outdoor power lines?
This is not recommended. AV wire is designed for fixed, protected indoor installations and lacks the required tensile strength and weather resistance for outdoor use. For overhead power transmission lines, you will need a specialized solution like aluminum 7 strand cable, which features a stranded structure designed to provide the necessary durability and safety.
5.2. How do AV cable and AXV cable differ?
Both have aluminum conductors, with the main difference lying in the insulation material. AV cable uses PVC insulation (operating temperature 70°C). While AXV cable uses XLPE (Cross-linked Polyethylene) insulation allowing higher operating temperature (90°C) and includes an additional outer PVC sheath.
5.3. Why is a larger cross-section needed when using aluminum cable?
Because aluminum's electrical conductivity is lower than copper (only 61% compared to copper). Therefore, to achieve the same electrical transmission capacity, aluminum cable needs a cross-section 1.6 times larger than copper cable.
5.4. Is AV cable suitable for residential electrical systems?
Technically, it is completely feasible. However, in practice, copper cable is preferred for indoor electrical systems due to ease of construction and stable connections. AV cable is suitable for main trunk lines and outdoor electrical distribution systems.
6. Conclusion
Through detailed analysis, what AV electrical wire is has been clearly explained: this is a low voltage power cable with aluminum conductor and PVC insulation, complying with TCVN 5935-1 and TCVN 6612 standards with voltage rating of 0.6/1kV. Comparison with copper CV cable shows that AV cable saves 30-40% investment cost and is 70% lighter in weight, although it requires a cross-section 1.6 times larger for the same load capacity.
Benefits of mastering this knowledge:
- Select the right cable type according to specific project conditions
- Optimize investment costs while ensuring technical safety
- Understand installation requirements to avoid damage during construction
Are you looking for consultation on selecting suitable electrical cable for your project? Contact Ngoc Lan Cable immediately for professional technical support and receive detailed quotations for your specific needs!
 VN
VN