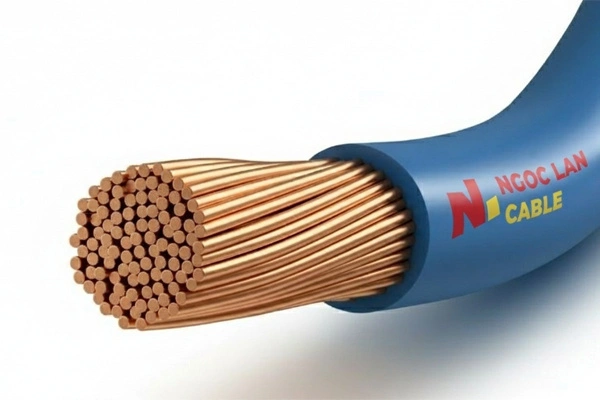
Have you ever wondered why the electrical wires in your home have the CV marking? Or why electricians often recommend using CV cables for residential electrical systems? In this article, we'll explore in detail about PVC insulated copper cable – one of the most common types of electrical wires today.
1. What is PVC insulated copper cable?
PVC insulated copper cable (CV) is a common type of electrical conductor widely used in residential and industrial electrical systems. With a structure consisting of a copper core and PVC insulation layer, CV cable ensures good electrical conductivity, safety, and durability in various harsh working conditions.
Why is PVC insulated copper cable so important?
First, conductors are essential components in every electrical circuit, responsible for transmitting electrical power from the source to consuming devices. A fault in the conductor can cause the entire system to stop working or create risks of electric shock and fire. Therefore, understanding the structure and characteristics of the wire will help you choose and use the product correctly, safely, and effectively.
2. Structure and Technical Specifications of PVC Insulated Copper Cable
To better understand PVC insulated copper cable, we need to examine its structure and technical specifications in detail.
2.1. Structure of PVC Insulated Copper Cable
PVC insulated copper cable consists of 2 main parts:
- Copper conductor core (¹): Usually made of solid pure copper or stranded from multiple thin wires. The cross-section determines the rated current that the cable can carry. Common cross-sections range from 4mm² to 500mm², depending on usage requirements.
- PVC insulation layer (²): Polyvinyl Chloride coating outside the copper core, which functions to isolate electrical current from the external environment, preventing electrical leakage and short circuits. PVC also has good resistance to impact, moisture, and high temperatures. Colors: Diverse, typically black, red, orange, blue, or yellow-green (for grounding).
Additionally, some PVC insulated copper cables have an extra protective outer layer made of hard PVC or abrasion-resistant nylon to enhance durability when installed outdoors or in harsh environments.
2.2. Technical Specifications
PVC insulated copper cables have the following important technical parameters:
- Rated voltage: These cables are typically designed for rated voltages from 300/500V, 450/750V to 0.6/1kV
- Operating temperature: Maximum 70°C
- Test voltage: 3.5 kV (for 5 minutes)
- Maximum permissible temperature during short circuit:
- 160°C (for cross-sections less than or equal to 300mm²)
- 140°C (for cross-sections greater than 300mm²)
3. Advantages and Disadvantages of PVC Insulated Copper Cable
Each type of electrical wire has its own characteristics, and PVC insulated copper cable is no exception. Let's examine its advantages and disadvantages to better understand this type of cable.
3.1. Advantages of PVC Insulated Copper Cable
- Excellent conductivity: Selecting the right copper core cross-section ensures efficient electrical transmission and reduces power loss.
- High safety: The PVC insulation layer provides excellent electrical insulation, minimizing the risk of electrical leakage and short circuits.
- High durability: PVC insulated copper cable can withstand various environmental factors such as temperature and humidity (if not too extreme).
- Easy installation: With good flexibility, PVC insulated copper cable is easy to bend and route through corners during installation.
- Reasonable cost: Compared to other cable types like CXV or CV/FR fire-resistant cables, PVC insulated copper cable offers good value for money.
- Diverse sizes and colors: Available in various cross-sections and colors, suitable for different applications.
3.2. Disadvantages of PVC Insulated Copper Cable
- Limited heat resistance: Not suitable for environments with continuous temperatures above 70°C.
- Not suitable for harsh environments: Should not be used in areas with corrosive chemicals or constant mechanical stress. PVC may age and crack after long-term use (over 10-20 years) outdoors.
- Lower flame retardant properties compared to specialized cables: While designed to limit flammability, standard PVC insulated copper cable is not specifically designed for flame retardance and may produce toxic smoke when burning.
- Not suitable for high voltage: Only appropriate for low voltage applications under 1kV, not suitable for high voltage systems.
- Poor electromagnetic interference resistance: Not the optimal choice for applications requiring EMI shielding.
Overall, PVC insulated copper cable remains an optimal choice for many standard electrical applications with reasonable investment costs. However, for special projects, careful consideration is needed to select the appropriate insulation material.
4. Practical Applications of PVC Insulated Copper Cable
PVC insulated copper cable is widely used in both industrial and residential applications. It's the preferred conductor type for fixed installations in various locations such as wall conduits, floor conduits, and ceiling conduits. Let's explore these applications in detail.
4.1. In Residential Electrical Systems
- Home electrical systems: PVC insulated copper cable is widely used in household wiring. It connects devices such as switches, outlets, and lighting fixtures. These cables are commonly used for low and medium-power electrical circuits in homes.
- Offices and commercial buildings: In offices, PVC insulated copper cable provides power to lighting systems, computers, and other office equipment. It's also used in air conditioning and ventilation systems of buildings.
- Public facilities: PVC insulated copper cable is used in schools, hospitals, and other public buildings for basic electrical systems. It's also used in public lighting systems such as street lights and garden lighting.
4.2. In Industrial Applications
- Manufacturing facilities: PVC insulated copper cable supplies power to low and medium-power machinery and equipment. It's also used in industrial lighting systems.
- Control systems: In automated control systems, PVC insulated copper cable connects sensors and controllers. It's also used in control panels for industrial machinery.
- Special applications: In some cases, PVC insulated copper cable is used in small-scale solar energy systems. It can also be used in certain outdoor applications with proper covering, provided there's no direct exposure to sunlight and severe weather conditions.
5. Installation Methods for PVC Insulated Copper Cable
Proper installation of PVC insulated copper cable ensures both safety and efficiency. Below are common installation methods and specific guidelines for each method.
5.1. Installation Methods
- Concealed wall installation: The cable is run through plastic or steel conduits, then embedded in walls. This method helps conceal electrical wiring, creating high aesthetic value for the building.
- Surface mounting: The cable is directly mounted on walls or ceilings using fixing clips. This method is commonly used in industrial facilities or technical areas.
- Cable tray installation: The cable is placed in metal or plastic cable trays. This method is suitable for office spaces or industrial warehouses.
- Underground installation: The cable is run through protective conduits and buried underground. This method is typically used for outdoor electrical systems or connections between buildings.
5.2. Installation Guidelines and Precautions
- Preparation: Thoroughly inspect the cable before installation, ensuring there are no cracks or damage to the insulation layer. Prepare necessary tools such as wire cutters, wire strippers, electrical tape…
- Installation: Follow regulations regarding minimum bending radius to avoid damaging the cable. Use accompanying accessories like conduits and cable trays for protection. Ensure connections are secure and properly insulated.
- Post-installation inspection: Use an insulation resistance meter to check the cable's insulation condition after installation. Verify all connection points to ensure there are no loose connections.
6. How to Select the Appropriate PVC Insulated Copper Cable
Selecting the right PVC insulated copper cable for your project is crucial. It affects not only operational efficiency but also directly relates to safety. Here are important criteria to consider when selecting PVC insulated copper cable:
6.1. Selection Criteria
Cable cross-section:
The cross-section depends on the expected current flowing through the cable.
Calculation formula: S = I / J (where S is the cross-section, I is current intensity, J is permissible current density).
For example: With a 20A current and permissible current density of 2.5A/mm², the required cable cross-section is 8mm².
Operating voltage:
- Standard PVC insulated copper cables are suitable for 300/500V, 450/750V, and 0.6/1kV.
- Select cables with rated voltage appropriate for the system's operating voltage.
Operating environment:
- Consider ambient temperature, humidity, and other factors that may affect the cable.
- Example: In high-temperature environments, select PVC insulated copper cable with better heat resistance.
Purpose of use:
- Clearly identify the intended use: for lighting systems, power supply to equipment, or control circuits.
- Each application may require specific types of PVC insulated copper cable with particular characteristics and colors.
Note that these criteria are for reference only. For safety and stability, if you don't have extensive electrical knowledge, it's recommended to consult a professional installation service.
6.2. Brands and Quality
Did you know that selecting the correct cable cross-section not only ensures safety but can also help save long-term costs? Cables with too small cross-sections can cause significant power losses, while oversized cables result in unnecessary expenses. Accurate calculation and selection will provide the best economic efficiency.
When choosing PVC insulated copper cable, selecting a reputable brand is also crucial. Some highly rated brands in the market include:
- Cadivi: Known for its large distribution system and diverse residential electrical wire products.
- Ngoc Lan Cable: Famous for durability, high quality, and diverse specialized power cables.
- Co Dien Tran Phu: Known for consistent quality and competitive pricing.
Notes for buying PVC insulated copper cable from dealers/stores: Even with genuine cables, some brands may “unintentionally” name their product models similar to conductor cross-sections, which even sellers may not notice. You need to read product specifications (with units) carefully to select accurately.
Common confusion examples:
- Cable with actual cross-section of 3.5mm²
- But packaging shows model number as CV 4.0
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
7.1. Where can PVC insulated copper cable be used?
PVC insulated copper cable is widely used in residential and light industrial electrical systems. Specifically, it's suitable for:
- Electrical systems in homes and offices
- Lighting circuits
- Power supply for low and medium-power electrical devices
- Some industrial factory applications
7.2. Can PVC insulated copper cable be used outdoors?
PVC insulated copper cable is not specifically designed for outdoor installation. If outdoor use is necessary, you should:
- Place the cable in specialized protective conduits
- Avoid direct exposure to sunlight and weather elements
- Consider using specialized outdoor cables like CVV or CXV
7.3. Comparison between PVC insulated copper cable (CV) and CXV cable?
PVC insulated copper cable and CXV power cable have several key differences:
Structure: PVC insulated copper cable has one PVC insulation layer, while CXV cable has two insulation layers
Moisture resistance: CXV cable has better moisture resistance than PVC insulated copper cable
Application: PVC insulated copper cable is mainly for indoor use, while CXV cable can be used both indoors and outdoors
Cost: CXV cable is typically more expensive than PVC insulated copper cable due to its more complex structure
7.4. How to check the quality of electrical cables?
To check the quality of PVC insulated copper cable, you can:
Visual inspection: Check the insulation layer, ensure there are no cracks or scratches
Insulation resistance measurement: Use specialized meters to test insulation capability
Conductivity test: Measure the conductor core resistance
Quality certification verification: Check certifications from authorized bodies
Note: In-depth testing should be performed by experts or specialized laboratories to ensure accuracy.
8. Conclusion
When selecting and installing PVC insulated copper cable, always remember that safety is the most important factor. Proper use of PVC insulated copper cable not only protects people and property but also contributes to improved electrical efficiency and long-term cost savings.
Finally, whether you're an electrical expert or a regular consumer, keeping up-to-date with knowledge about electrical cables in general and PVC insulated copper cable, in particular, is essential. Technology and safety standards are constantly evolving, so always seek the latest information to ensure you're using the best products for your needs.
We hope this article has provided you with useful information about PVC insulated copper cable. Remember, whenever you have any doubts about choosing or installing electrical cables, don't hesitate to consult experts in this field.
 VN
VN



