3 phase 4 core aluminum electrical cable plays a crucial role in industrial power transmission systems. Choosing the right cable type not only helps optimize investment costs but also determines the durability of the entire industrial electrical system. Especially in Southern and Central Vietnam with harsh climate conditions, durability requirements become even more important.
The main content of this article will present:
- Latest reference price table with common cross-sections and project discount rates
- 3-step guide to choosing appropriate cable cross-section
- Comparison between aluminum and copper cables to make suitable decisions for projects
Besides the core information above, engineers and contractors often raise deeper technical questions: What is the allowable voltage drop limit for low-voltage cables in Vietnam, how to handle aluminum cable joints to prevent oxidation, is twisted aluminum cable (ABC) a 3 phase 4 core cable?
The article below will help us answer each of these questions with professional insights from leading industry experts.

1. Latest price list for 3 phase 4 core aluminum electrical cable
Before diving into technical details, understanding pricing information is the primary deciding factor for any project. The actual price of 3 phase aluminum cable can fluctuate depending on timing, order volume, and market factors. For large-scale projects, contractors often receive significant discounts from manufacturers.
Simplified price table for common cross-sections:
| Cross-section (mm²) | Structure | Reference price (VNĐ/m) |
|---|---|---|
| 3×25+1×16 | AL/XLPE/PVC | Contact us |
| 3×50+1×25 | AL/XLPE/PVC | Contact us |
| 3×70+1×35 | AL/XLPE/PVC | Contact us |
| 3×95+1×50 | AL/XLPE/PVC | Contact us |
| 3×120+1×70 | AL/XLPE/PVC | Contact us |
| 3×150+1×95 | AL/XLPE/PVC | Contact us |
Note on price fluctuations: Global aluminum raw material prices and USD/VND exchange rates directly impact product costs. We encourage customers to contact Ngoc Lan Cable directly for accurate cable pricing and better deals with favorable discount rates.
2. 3-step guide for selecting 3 phase aluminum cable cross-section according to technical standards
Selecting the cross-section for 3 phase electrical cable requires a careful calculation process. Many engineers, especially those new to the profession, often make basic mistakes by relying solely on personal experience or applying the “oversized selection” principle without scientific basis.
The 3-step process detailed below is relatively basic and easy to apply. These steps are suitable for both electrical engineers and procurement staff who need to understand technical requirements clearly.
2.1. Step 1: Determine actual working current of the load
This is considered the most important step and also the point where many people commonly encounter errors.
Standard calculation formula for 3-phase loads:
I = P / (√3 × U × cosφ × η)
Where:
- P: Actual load power (W)
- U: Line voltage (commonly 380V in Vietnam)
- cosφ: Power factor (typically 0.8-0.9 for industrial equipment)
- η: Equipment efficiency (0.85-0.95 depending on machinery type)
Real-world calculation example for a small production workshop:
Suppose a garment factory has an industrial air compressor system with technical specifications: P=30kW, cosφ = 0.85, η = 0.9
Current calculation for the air compressor:
I = 30,000 / (1.732 × 380 × 0.85 × 0.9) = 59.6A
Important technical note: For loads with heavy starting characteristics like industrial motors, multiply by a starting factor from 1.1 to 1.25. This ensures the cable doesn't get overloaded during equipment startup phase.
2.2. Step 2: Look up allowable current and select preliminary cross-section
After determining the working current, the next step is to look up the allowable current based on specific installation conditions. This lookup needs to be based on manufacturer catalogues and specialized technical documents.
Basic selection principle: The cable's allowable current must be greater than or equal to the actual working current.
Example below applies to 30kW air compressor (I = 59.6A)
Look up common cross-sections from specialized technical catalogues:
- AXV 3×50+1×35 cable has allowable current ≈ 146A
- AXV 3×70+1×50 cable has allowable current ≈ 187A
Comparative analysis with actual working current:
- Cross-section 3×50+1×35: 146A > 59.6A → Meets basic technical requirements
- Cross-section 3×70+1×50: 187A > 59.6A → Meets requirements with higher reserve
To ensure absolute safety and create reserve for future load expansion capability, it's recommended to choose cable with allowable current significantly higher than current working current. The suggested preliminary choice is AXV 3×70+1×50 cable.
Important note: This is only the preliminary selection step based on cable capacity. The final cross-section must be confirmed through voltage drop checking to ensure stable and efficient operation of the entire system.
2.3. Step 3: Check voltage drop conditions
Many engineers in practice often overlook or underestimate the importance of this step, leading to serious consequences later. Voltage drop exceeding allowable limits not only reduces equipment operating efficiency but can also cause overheating, abnormal vibration, and potential fire and explosion risks in electrical systems.
Serious impacts of excessive voltage drop:
- Significantly reduces equipment lifespan due to continuous operation under low voltage
- Increases working current, leading to serious overheating in conductors
- Causes difficulties during industrial motor startup processes
- Reduces overall energy efficiency of the system
Voltage drop checking formula
ΔU% =K x lb x L
Where:
- L: Total cable length (m)
- Ib: Maximum working current
- K: coefficient from reference table
| Voltage drop table ΔU for 1 Amp per 1km cable length (V) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-section (mm²) | Single phase circuit | 3-phase balanced circuit | |||||
| Copper | Aluminum | Motor power | Lighting | Motor power | Lighting | ||
| Operation cosφ=0.8 | Start up cosφ=0.35 | Operation cosφ=0.8 | Start up cosφ=0.35 | ||||
| 1.5 | 24.00 | 10.60 | 30.00 | 20.00 | 9.40 | 25.00 | |
| 2.5 | 14.40 | 6.40 | 18.00 | 12.00 | 5.70 | 15.00 | |
| 4 | 9.10 | 4.10 | 11.20 | 8.00 | 3.60 | 9.50 | |
| 6 | 10 | 6.10 | 2.90 | 7.50 | 5.30 | 2.50 | 6.20 |
| 10 | 16 | 3.70 | 1.70 | 4.50 | 3.20 | 1.50 | 3.60 |
| 16 | 25 | 2.36 | 1.15 | 2.80 | 2.05 | 1.00 | 2.40 |
| 25 | 35 | 1.50 | 0.75 | 1.80 | 1.30 | 0.65 | 1.50 |
| 35 | 50 | 1.15 | 0.60 | 1.29 | 1.00 | 0.52 | 1.10 |
| 50 | 70 | 0.86 | 0.47 | 0.95 | 0.75 | 0.41 | 0.77 |
| 70 | 120 | 0.64 | 0.37 | 0.64 | 0.56 | 0.32 | 0.55 |
| 95 | 150 | 0.48 | 0.30 | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.40 |
| 120 | 185 | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.23 | 0.31 |
| 150 | 240 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.27 |
| 185 | 300 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.20 |
| 240 | 400 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.16 |
| 300 | 500 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.13 |
3. Quick comparison between aluminum and copper cables: When should you choose aluminum?
To make the right investment decision, understanding the clear differences between aluminum and copper cables is essential. From experience consulting thousands of projects, industry experts recognize that aluminum cables have absolute advantages in cost and weight, but require larger cross-sections and more technical joint handling compared to copper cables.
Three main differences:
- Cost: Aluminum cables are 40-60% cheaper than copper cables of the same power capacity, particularly important for large-scale projects.
- Weight: Significantly lighter, helping reduce transportation and installation costs, especially beneficial for overhead lines.
- Technical requirements: Need approximately 60% larger cross-section and professional joint handling techniques to prevent oxidation.
Cases where aluminum cables should be prioritized:
- Medium and long-distance overhead transmission lines
- Residential construction projects requiring cost optimization
- Power distribution systems in industrial zones
- Temporary applications or those with short replacement cycles
For deeper understanding of performance analysis, durability, and detailed application cases, please refer to our comprehensive article: Detailed comparison between aluminum and copper core electrical cables for a complete overview of each product type.
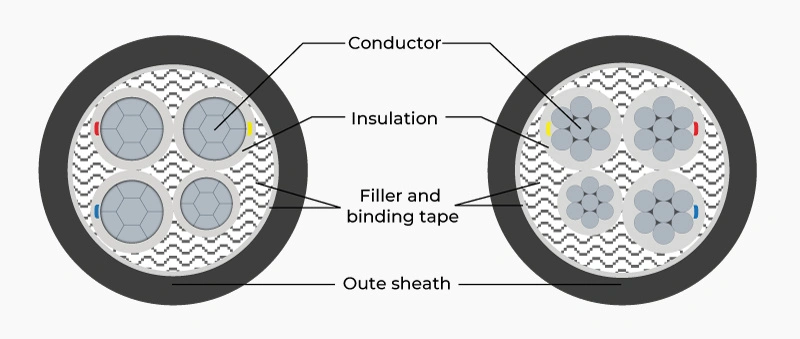
4. Technical specifications & structure of 3 phase 4 core aluminum cable
Understanding the structure of 3 phase 4 core aluminum electrical cable is a crucial factor helping engineers and contractors make the right choices. The multi-layer structure of aluminum cables is optimally designed to ensure safety, performance, and durability in harsh operating environments.
4.1. Detailed layer-by-layer structure
- Electrical conductor core: Aluminum core is concentrically stranded or concentrically stranded and compressed tight to create flexibility and increase load-bearing capacity
- XLPE insulation layer (Cross-linked Polyethylene): XLPE sheath can withstand temperatures up to 90°C under normal operating conditions and 250°C in short-term situations.
- Filler and tape wrapping layer: Usually filled with PP fiber and tape-wrapped to create uniform roundness for the cable.
- PVC outer sheath: PVC outer sheath layer protects the entire cable from environmental impacts.
4.2. Applied technical standards
National and international standards:
- IEC 60502-1/ TCVN 5935-1
- IEC 60228/ TCVN 6612
Important technical characteristics:
- Rated voltage (Uo/U): 0.6/1kV.
- 50Hz test voltage for 5 minutes: 3.5kV.
- Maximum rated operating temperature of conductor core: 90ºC.
- Maximum short-circuit temperature in 5s of conductor core: 250ºC
4.3. Role of the neutral wire
The neutral wire in the 4-core structure plays an important role in load balancing and ensuring system safety. This fourth core usually has the same cross-section as the phase cores or smaller depending on design requirements.
Main functions:
- Balancing current under conditions where current flowing through phases is unbalanced
- Ensuring phase voltage stability in 3-phase 4-wire systems
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
5.1. Is twisted aluminum cable (ABC) a 3 phase 4 core cable?
No. Aerial Bundled Cable (ABC) is a completely different type of cable compared to conventional 3 phase 4 core aluminum cable.
ABC has a special structure with cores twisted together without outer sheath, while 3 phase 4 core aluminum electrical cable has a structure of 4 cores twisted together and contained within the same outer sheath.
5.2. How to handle aluminum cable joints to prevent oxidation?
Apply the standard 4-step technical process to ensure durable and long-term safe joints.
Oxidation phenomenon is the biggest challenge with aluminum cables, which can cause increased resistance and dangerous overheating. The proper handling process will completely eliminate this problem:
- Step 1: Clean the aluminum surface with fine sandpaper to remove the natural oxidation layer
- Step 2: Apply anti-oxidation gel immediately after cleaning
- Step 3: Use specialized aluminum lugs with appropriate compression force
- Step 4: Provide complete insulation wrapping and periodically check joint quality
Important note: Never use copper lugs with aluminum cables due to different expansion coefficients.
5.3. What is the allowable voltage drop limit in low-voltage networks in Vietnam?
The most common general regulation in Vietnam for voltage drop in low-voltage networks is not to exceed 5% compared to the rated voltage at the connection point with electricity-using customers under normal operating conditions (Circular 39/2015/TT-BCT).
6. Conclusion and free technical consultation
When you need to choose 3 phase 4 core aluminum electrical cable, the first step is to survey pricing to get appropriate costs. Then, you need to perform accurate cross-section calculations and thoroughly understand essential technical parameters. Through the detailed 3-step process guided above, you will be able to select the most optimal cable type for your project.
Summary of key points:
- Method of calculating actual working current combined with looking up allowable current
- Voltage drop checking to ensure safety during transmission.
- Comparison of advantages and disadvantages between aluminum and copper cables helps optimize investment costs and ensure performance.
Benefits when applying this guide:
- Save 20-30% investment costs through correct cross-section selection
- Ensure system safety with extended lifespan
- Avoid common technical mistakes
Do you still have technical questions or need detailed quotations for specific projects? Ngoc Lan Cable's team is always ready to support 24/7. Contact us immediately to receive the most optimal solution advice for your needs!
 VN
VN