Incorrect selection of single-core wire not only causes voltage drop up to 20% but also poses serious overheating risks for the entire M&E system. Additionally, confusion between rigid single core wire and flexible single core wire often creates numerous difficulties during installation.
This article analyzes 8 technical criteria from Ngoc Lan Cable's expert team to help engineers make accurate decisions:
- Definition according to TCVN 6610 standard and core structure of single core wire
- Classification by conductor structure (rigid/flexible)
- Comparison of 8 technical criteria with multi-core wire for appropriate selection
- Applications from residential to industrial settings
Understanding the definition of wire is the first step to grasping the structure and operating principle of this wire type.
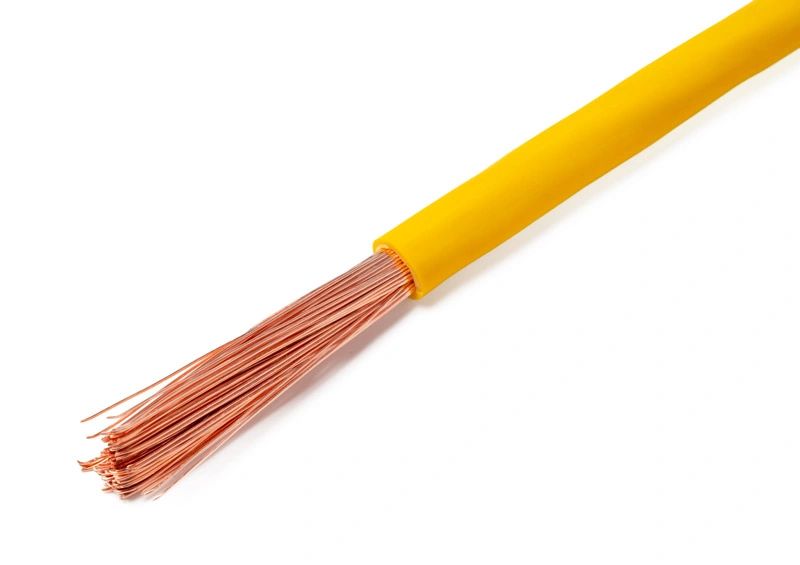

1. Single-Core Wire: Structure according to TCVN 6610 standard and applications
Single-core wire is a type of conductor that has only one conductive core, surrounded by an insulation layer according to TCVN 6610 standard (equivalent to IEC 60227). This simple structure creates a fundamental difference compared to multi-core cable types in electrical systems. The conductor is typically made from copper or aluminum, with the surrounding insulation layer made from PVC plastic.
Main technical characteristics:
- Simple conductor structure: A single solid copper or aluminum wire for rigid wire or multiple small stranded wires for flexible wire
- Diverse cross-sections: From 1.5mm² to 240mm² meeting different power transmission requirements
- Rated voltage: 450/750V for residential applications, 0.6/1kV for industrial applications
- Operating temperature: 70°C under normal operating conditions
- Standard designation: CV (Cu/PVC), VC (rigid wire), VCm (flexible wire) according to Vietnamese market convention
With such stringent technical requirements, selecting a reputable manufacturer is the decisive factor for long-term quality. Ngoc Lan Cable's single-core wire products (CV wire, AV wire) strictly comply with testing procedures, ensuring quality before leaving the factory.
Important note: A detailed comparison between single-core wire and multi-core wire will help engineers clearly understand the advantages and disadvantages of each type. Each wire type has distinct characteristics regarding mechanical durability as well as transmission efficiency. The next section will analyze 10 important technical criteria so you can select the appropriate wire type for each specific application.
2. Classification of single-core wire by structure
Choosing a wire type that is not suitable for application requirements can cause overload on the electrical conduction system. Therefore, engineers need to clearly understand the classification of single-core wires to help identify the correct product for the project category.
Classification by conductor structure:
- Rigid single wire (VC): The conductor is a single solid copper wire, PVC insulation, applied according to TCVN 6610-3 standard. This is the wire type with the highest mechanical durability, suitable for fixed wiring, used in conduits embedded in walls. The advantage is good impact resistance and minimal deformation over time, while the disadvantage is difficult to bend when installing in tight corners. Ngoc Lan Cable rigid VC wire products have various cross-sections from 0.5mm² to 10mm².

- Flexible single wire (VCm): The conductor is stranded from multiple copper wires with very small diameter, PVC insulation. The wire has high flexibility, suitable for connecting equipment and electrical panels. The advantage is easy installation and the disadvantage is individual small strands are prone to breakage in corrosive environments. Ngoc Lan Cable flexible VCm wire products have cross-sections from 0.5mm² to 240mm² with optimal flexibility.

3. Technical comparison of single core wire and multi-core wire based on 10 criteria
Understanding the differences between single core wire and multi-core wire through the 10 criteria below helps engineers make accurate decisions.
Multi-core wire is a cable with 2 or more conductors within a common outer sheath. Each core has its own insulation with different colors.
Detailed comparison table:
| Criteria | Single core wire | Multi-core wire |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | One conductor + 1 insulation layer | 2-5 separate conductors + common outer sheath |
| Mechanical strength | 30-40% higher | Lower |
| Flexibility | Low (rigid wire) to medium (flexible wire) | High, easily bent in confined spaces |
| Transmission performance | Stable and efficient transmission across wide frequency range, minimal energy loss | Less stable, higher energy consumption |
| Material cost | 8-12% lower due to simpler manufacturing process | Higher due to multiple cores and complex sheath |
| Installation cost | Higher if multiple separate wires are needed | Lower due to bundled cores, faster installation |
| Conductor termination | Simple, time-efficient, easy maintenance | Complex, requires high technical skill to separate individual cores |
| Primary applications | Fixed wiring, earthing, high power applications | Control systems, 3-phase motors, portable cables |
Selection decision based on application:
Selecting the appropriate cable type depends on the specific requirements of each application. For standard residential electrical systems, single core wire is the optimal choice due to reasonable cost and adequate performance for intended use. Meanwhile, projects with high operating capacity should prioritize multi-core cables to ensure stable electrical power transmission and enhance safety during operation.
4. Applications of single core wire in residential and industrial projects
nderstanding the applications of single core wire helps ensure project safety. Therefore, this section analyzes the scope of use from residential to industrial applications.
Applications in residential and commercial projects:
- Fixed indoor wiring: Rigid single core wire is commonly applied for fixed installations such as running through conduits, from main distribution boards to intermediate junction boxes. High stability ensures 25-30 years of safety for the project.
- Earthing systems (PE/TE): Single core copper wire connects equipment to earth rods, providing protection against electrical leakage and lightning strikes.
- Public lighting: Power supply for lighting systems, run together in HDPE conduits buried underground.
Applications in industrial systems:
- Distribution panel connections: Flexible single core wire (VCm) connects switching devices with flexibility that enables neat installation within panels. This wire reduces mechanical stress on MCB and contactor terminals.
- UPS and battery systems: Large cross-section single core wire (50-95mm²) is used for DC connections from battery banks to UPS cabinets. Large cross-sections help reduce resistance, thereby limiting energy loss during transmission and ensuring capacity to withstand high discharge currents during mains power failure.
5. Frequently asked questions about single core wire
5.1. Is single core wire better than multi-core wire?
Neither type is absolutely better; each is suitable for different applications. Therefore, if a project requires durability for fixed installations, use single core wire; for flexibility with mobile equipment, use multi-core wire.
5.2. What factors does single core wire pricing depend on?
Pricing follows the global copper market on the LME exchange, which fluctuates daily. Larger cross-sections cost more due to higher copper content. Additionally, pricing depends on established and reputable brands, which are 5-10% more expensive than standard products.
5.3. Can single core wire be used for an entire house?
It is possible but not optimal in terms of cost and installation. It is recommended to combine rigid single core wire for fixed main lines, while flexible single core wire is more suitable for equipment connections.
6. Conclusion
Selecting the correct single core wire according to technical requirements ensures 25-30 years of project safety. Clearly distinguishing between rigid single core wire and flexible single core wire enables cost-effective and technically efficient electrical system installation.
Key points to remember:
- Structure: One copper/aluminum conductor + one PVC insulation layer
- Two main classifications: Rigid wire (VC) for fixed installations, flexible wire (VCm) for connections
- Durability advantage: 30-40% higher than multi-core wire, excellent corrosion resistance
- Avoid dangerous mistakes: Do not select cross-sections smaller than load requirements, comply with TCVN 7447 regarding selection and installation
Ngoc Lan Cable supplies single core wire products from 1.5mm² to 240mm². Products are suitable for all project scales from residential to industrial. Contact the technical department immediately for detailed consultation on appropriate selection or download the technical catalogue for complete specifications reference for your project.
 VN
VN