3-core wire ensure absolute electrical safety for modern equipment such as water heaters, air conditioners, and washing machines. Unlike traditional 2-core wire with only live and neutral wires, 3-core wire add a third core is the earth wire to protect users from electric shock. However, this core raises the most questions: How does it work? And when is it mandatory to use?
This article prepared by Ngoc Lan Cable's engineering team will clarify:
- Detailed 3-core wire structure and the role of each layer
- Distinguishing functions of 3 cores: live wire, neutral wire and earth wire
- Comparison between 3-core and 2-core wire to understand safety and anti-shock mechanisms
Additionally, you'll understand cable classification by purpose (portable domestic, fixed systems, industrial 3-phase), 3 criteria for selecting safe cables plus quality inspection tips without specialized tools, and answers to frequently asked questions about 3-core wire.
First, the basic definition and electrical accident statistics will help you clearly recognize the importance of using the correct cable type.
1. What is a 3-core wire?
A 3-core wire is a type of conductor consisting of three separate cores within a common outer sheath. The three cores include the live wire (Live/L), the neutral wire (Neutral/N), and the earth wire (Earth/E). Unlike traditional 2-core wire, the third wire is the earth wire, does not transmit electrical energy; instead, it protects users from electric shock.
When equipment experiences electrical leakage, the earth wire immediately conducts the leakage current to ground. The RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent protection) detects the fault within 0.03 seconds and automatically trips the circuit to protect users from electric shock hazards.
⚠️ SAFETY WARNING
According to Vietnam's Fire Prevention and Fighting Police Department, 74.4% of fires in Q1/2025 occurred due to electrical system failures. The main causes were using poor-quality conductors, lacking earth wires, or insufficient wire cross-sections causing severe electrical shorts. The year 2024 recorded 4,112 fires due to electrical systems not meeting safety standards.
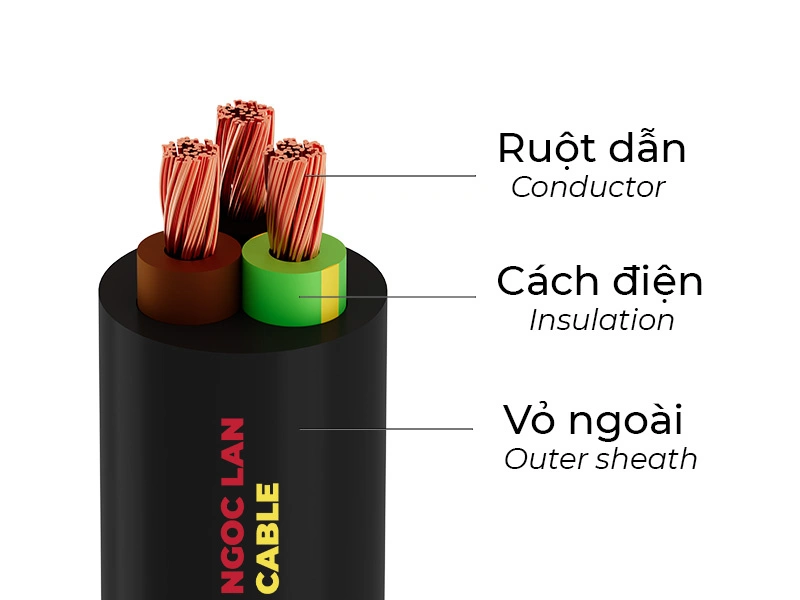
2. Detailed structure of 3-core wire
After understanding the role of 3-core wire, mastering their structure helps you identify quality products. The structure of 3-core wire comprises three main layers with different functions:
2.1. Conductor
This component carries electrical current from the source to equipment, typically made from pure copper, ensuring low resistance, which helps reduce power loss and limits heat generation.
Some cheap cables use aluminum or copper alloys. These types have resistance 1.6 times higher than pure copper, easily causing wire heating and increasing fire and explosion risks.
2.2. Insulation
Each core is individually wrapped with specialized insulating material. Standard PVC plastic withstands 70°C, suitable for common household electricity. Premium XLPE material withstands up to 90°C and is used for harsher environments.
The insulation layer prevents short circuits between conductors while protecting the copper conductor from oxidation over time.
2.3. Outer sheath layer
The outer PVC sheath protects all three cores from mechanical impacts, prevents collision damage, and resists moisture and environmental chemicals. The outer sheath's lifespan can extend up to 25 years. At Ngoc Lan Cable, we manufacture outer sheaths using flame-retardant PVC plastic according to IEC 60332-1.
3. Distinguishing the functions of 3 cores: live wire, neutral wire, and earth wire
Each core has different functions and is color-coded according to international IEC standards. Therefore, it's essential to understand the color coding to avoid confusion between cores, which could lead to serious electric shock incidents.
Table distinguishing 3-core functions
| Name | Symbol | Function | Color | Danger level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Live wire | L (Live) | Carries 220V phase voltage, transmits | Brown/Black/Red | Causes shock, life-threatening |
| Neutral | N (Neutral) | Balances current, creates closed circuit with ~0V voltage | Blue | Safe when system operates normally |
| Earth | E (Earth) | Conducts leakage current, kích hoạt bộ bảo vệ RCBO | Xanh lá sọc vàng | Bảo vệ chống giật tuyệt đối |
The live wire (L) carries dangerous 220V voltage; direct contact with this wire causes serious electric shock. Its main function is to transmit energy from the power source to equipment, with identifying colors being brown, black, or red.
The neutral wire (N) has nearly 0V voltage under normal operating conditions. It helps balance current in the circuit and creates a closed loop. Current flows from the live wire through equipment and returns to the source via the neutral wire. The identifying color is blue.
The earth wire (E) doesn't transmit electricity under normal conditions. When equipment leaks electricity to the metal casing, this wire immediately conducts the leakage current to ground. The RCBO detects the current difference between live and neutral wires, tripping the circuit within 0.03 seconds to protect users. Green with yellow stripes is the color used for earth wire.
Important note about “cold wire”
Many people mistakenly call the earth wire “cold wire.” In electrical engineering, “cold wire” is the common term for neutral wire (N), which is blue and has nearly 0V voltage. The earth wire (E) is completely different with green and yellow stripes. These two wires have entirely different functions in the electrical system.
4. Comparison between 3-core wire and 2-core wire
Understanding the special function of the earth core, you'll see the important difference between 3-core wire and traditional 2-core wire.
- A 2-core wire only includes live and neutral wires. When equipment like water heaters experience electrical leakage, the metal casing becomes dangerously electrified, and people touching the equipment casing get shocked because there's no safe path for the leakage current.
- A 3-core wire adds an earth wire that creates an “escape path” for leakage current to be conducted to ground instead of passing through the human body. The RCBO then detects the leakage current within 0.03 seconds and automatically trips the circuit to fully protect users.
All equipment with metal casings must use 3-core wire combined with RCBO to ensure user safety. This is the proactive electrical safety standard that Ngoc Lan Cable's technical experts recommend implementing.
5. Classification and applications of 3-core wire by purpose
Although 3-core wire are safer than 2-core wire, not all 3-core wire are suitable for every purpose. Classifying 3-core wire by application helps avoid dangerous mistakes. Each type has distinct construction and technical specifications.
5.1. Portable domestic cables (VCmt, VCmo)
VCmt cables feature multi-strand flexible copper conductors twisted together, with flexible PVC sheathing that increases flexibility. They're suitable for frequently moved portable equipment such as electric fans, rice cookers, extension sockets, and handheld devices.
5.2. Fixed installation cables (CVV)
CVV cables have a rigid structure with thick, durable PVC sheathing. The CVV designation stands for C (copper conductor) + V (PVC insulation) + V (PVC outer sheath). This cable type offers durable mechanical strength, long service life, and good moisture resistance when installed in conduits or embedded in walls.
This is the standard choice for fixed domestic electrical installations. Water heaters, air conditioners, refrigerators, and washing machines all require CVV cables. Residential and office construction projects use this cable type for entire in-wall electrical systems.
5.3. Industrial 3-phase cables
Industrial cables have 4-5 cores with special construction. Three live cores carry three electrical phases, one neutral core, and one earth core. Large cross-sections from 2.5mm² to 240mm² handle high loads. This cable type serves 380V industrial electricity for motors, pumps, and conveyor belts.
Factory electrical panels and industrial machinery systems require this cable type. Note that the 3-core cable in this article refers to single-phase domestic type, while industrial 3-phase cables typically have 4-5 cores with completely different construction.
6. How to select 3-core wire and inspection tips
After distinguishing 3-core wire types for each purpose, you need to know how to select quality products to avoid overload and fire hazards. The three criteria and inspection tips below help you choose safe cables.
6.1. Three technical selection criteria
Select correct cable cross-section matching power capacity
Cable conductor cross-section must be selected proportionally to equipment power usage. For example:
- 1HP air conditioner (9,000 BTU) needs 3×1.5mm² cable.
- 2HP air conditioner (18,000 BTU) requires 3×2.5mm² cable.
If the cable cross-section isn't large enough, the system will experience severe overload. When conductors overload, temperature rises beyond safe thresholds, causing PVC insulation to become brittle and prone to cracking. This leads to increasing risk of electrical shorts and fires over usage time.
Prioritize copper conductors
Prioritize selecting 3-core wire with copper conductors because copper has resistivity of 0.017241 Ω.mm²/m at 20°C, providing good conductivity and low heat generation. Meanwhile, aluminum cables have resistance 1.6 times higher than copper, easily heating up and causing significant power loss.
Choose manufacturers with complete certification
Products must have Certificate of Origin (CO) and Certificate of Quality (CQ) to ensure quality. Additionally, they must have anti-counterfeit stamps and clear warranty documents ensuring user rights. At Ngoc Lan Cable, we provide complete certifications along with testing documentation from accredited laboratories.
6.2. Three quality inspection tips without special tools
Tip 1 – Inspect copper conductor
Strip a small section to directly observe the copper core. Bright orange-red color indicates high-quality pure copper, while pale yellow or dull color indicates copper alloy.
Gently twist the copper core by hand with moderate force. Pure copper is flexible and doesn't break when twisted. Poor-quality copper is stiff and breaks easily after a few twists.
Tip 2 – Test insulation layer
Stretch the PVC sheath with moderate force using both hands. High-quality PVC is flexible and stretches 2-3 times its length, while poor-quality sheath is brittle and breaks immediately.
Bend the cable section repeatedly at the same position. Good PVC sheath doesn't crack or lose elasticity, while poor-quality sheath shows cracks after a few bends.
Tip 3 – Compare actual cross-section
Place the cable to be tested next to a same cross-section cable from a reputable manufacturer and visually compare the copper core diameter. If noticeably smaller, the cable has insufficient cross-section.
You can use an electronic scale to weigh 1 meter of cable and compare weight with technical catalog. Under-sized cable weighs 15-20% less than standard cable.
7. Frequently asked questions about 3-core wire
7.1. Is "cold wire" the same as earth wire?
Answer: Absolutely incorrect in professional electrical engineering. “Cold wire” is the common term for neutral wire (N) which is blue colored. It balances current in the circuit and has nearly 0V voltage. The earth wire (E) has green with yellow stripes and is completely different.
The neutral wire completes the electrical circuit loop enabling equipment operation. The earth wire protects users by conducting leakage current to ground. These two wires have entirely different functions.
7.2. My home only has 2-core wire, how can I safely use 3-pin sockets?
Answer: Never cut the earth pin from equipment plugs, as this completely removes the shock protection function of 3-core wire.
The correct solution requires contacting a certified electrician with extensive experience. They will install standard earth rods, rewire complete 3-core wire routes from the main electrical panel, and install 30mA RCBO for comprehensive electrical system safety protection.
Ngoc Lan Cable's technical experts recommend this investment to ensure long-term family safety.
8. Electrical safety with quality 3-core wire
From definition, structure, and functions to classification and selection methods, you now have comprehensive knowledge about 3-core wire. 3-core wire are not an optional choice but a mandatory technical requirement ensuring electrical safety for equipment in every household. Understanding the structure, correctly classifying by purpose, and knowing how to inspect cables protects your family.
Three key points to remember about 3-core wire:
- Earth wire is essential, indispensable protection: The third core protects users by immediately conducting leakage current to ground. RCBO trips the circuit within 0.03 seconds upon detecting faults.
- Each cable type serves a specific purpose: Portable VCmt cables for frequently moved handheld equipment. Fixed CVV cables for in-wall installation of water heaters and air conditioners. 3-phase cables for industrial high-power motor electricity. Using the wrong type causes damage or dangerous fire hazards.
- Thoroughly inspect before purchasing: These three simple tips help avoid buying poor-quality cables:
- Test copper conductors for bright orange-red color and flexibility.
- Check PVC insulation layer for good flexibility and stretching capability.
- Compare cross-section with standard cables from reputable manufacturers.
When installing new electrical systems or renovating, prioritize consultation from certified electrical engineers. They calculate precise cable cross-sections matching total equipment power capacity. Proper investment in quality 3-core wire and standard earthing systems is a small expense that protects your family's assets throughout 20-25 years of use.
 VN
VN