- Definition and structure according to TCVN standards
- Comparison table of structure, applications, and durability
- Answers to frequently asked questions about selection and practical applications
Ngoc Lan Cable's objective is to help you distinguish between electrical wires and electrical cables, thereby choosing the right type of wire or cable for electrical projects, from residential to industrial systems.
1. Detailed definitions, structure, and classification
To accurately distinguish between electrical wires and electrical cables, clearly understanding the definition and structure of each type is the most important first step. Each type has distinct technical characteristics regulated by specific TCVN standards.
After mastering these basic concepts, you will be able to make accurate decisions for each specific application.
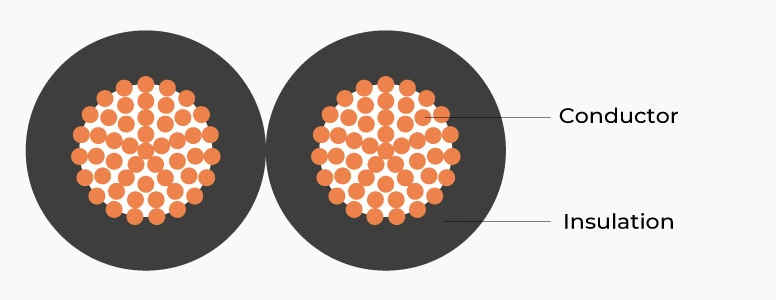
1.1. Definition and structure of electric wire
1.1.1 Definition and structure
Electric wire is a simple structure consisting of 1 or 2 metallic electrical conductor cores covered with an insulation layer.
Technical specifications according to standards:
According to TCVN 6612 standard, the conductor can be rigid type (class 1 – single strand) or flexible (class 5, 6 – multiple strands twisted together). The PVC sheath complies with TCVN 6610 ensuring safe insulation properties.
Technical parameters:
Electric wire has low resistance and is designed to transmit electric current with limited power. The working voltage rating is usually limited to 750V or 0.6/1kV. This product is typically installed in air or inside conduits for enhanced protection.
1.1.2 Detailed classification by structure:
Regarding classification, electric wires are divided into several common types as follows:
- Flexible single wire (Vcm)
- Rigid single wire (VC, VA)
- Stranded single wire (CV, AV)
- Flexible twin wire (VCmo, VCmt)
- Flexible flat wire (Twin flexible wire VCmd)
Materials and practical applications:
The conductor core material is usually copper. The insulation sheath is made from PVC with good moisture resistance and insulation properties. Residential electrical wires are mainly applied for indoor equipment, including lighting systems, TVs, refrigerators, and other household appliances.
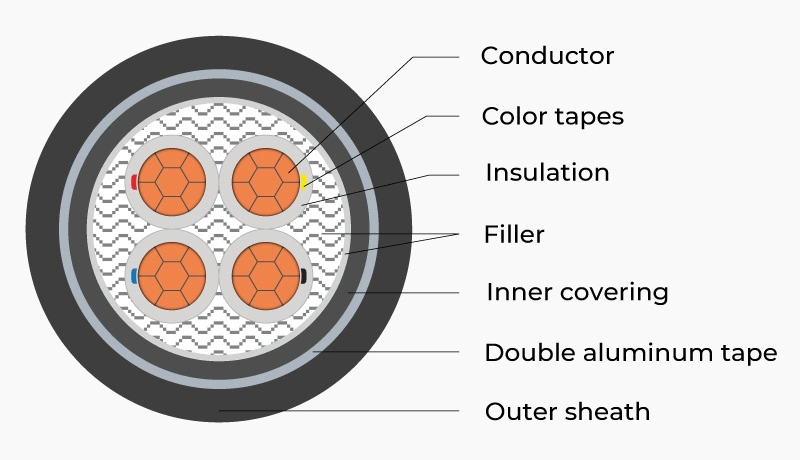
1.2. Definition and structure of electric cable
1.2.1. Definition and structure:
Electric cable is a cable type with much more complex structure, comprising one or multiple conductor cores with individual insulation sheaths. Then, all are collectively wrapped in multiple protective layers.
The conductor is usually class 2 (circular compacted stranded) according to TCVN 6612, ensuring stable electrical conductivity. The protective sheath is designed with multiple layers to resist mechanical impacts such as collisions and tensile forces. It simultaneously protects against environmental factors like humidity, high temperature, and chemicals.
Materials used:
- The conductor can be copper or aluminum
- The insulation layer uses PVC or XLPE insulation (Cross-linked polyethylene) – a material with superior heat resistance and insulation capabilities compared to PVC
- The armor tape layer against impacts can be 2 aluminum tape layers (DATA), 2 steel tape layers (DSTA), or steel wire armor (SWA)…
- The outer sheath can be PVC, XLPE, HDPE, or flame-retardant plastic materials like LSZH, FR-PVC…
Power cables have the ability to transmit large currents and high voltages, typically from 0.6/1kV and above.
1.2.2. Classification by application and voltage:
Classification by application:
- Control cables: Used for power transmission and controlling functions in machinery systems
- Power cables: Transmit high-power electrical energy, used in industrial projects such as cable trays, cable ladders, factories, buildings, underground installation
- Fire-resistant cables: Applied in projects requiring high fire safety standards
Classification by voltage level:
- Low voltage cables: 0.6/1kV
- Medium voltage cables: 6/10(12)kV, 12/20(24)kV
- High voltage cables: Above 35kV
Based on practical experience from implemented projects, choosing the right insulation material directly affects the lifespan and safety of the system.
After thoroughly understanding the detailed definitions and structures of each type, placing them on a comparison scale will help you make more accurate selections.
2. Overview comparison table: Electrical wires and electrical cables
To help engineers and contractors have a quick overview, we present the detailed comparison table below. This table summarizes the most core differences between the two product types based on data from successfully implemented projects.
| Comparison Criteria | Electric Wire | Electric Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Structure and Sheath | Simple, usually only 1 insulation layer | Complex, multiple protective layers. Each core has individual insulation |
| Typical Applications | Indoor use, distribution boards, household appliances, lighting systems | Industrial, high-power transmission, underground, in factories, harsh environments |
| Working Voltage Level | Low voltage networks (typically up to 0.6/1kV) | Low voltage, medium voltage, and high voltage networks (from 0.6/1kV and above) |
| Durability and Lifespan | Easily affected by mechanical impacts, lower durability | Impact resistant, good waterproofing, high durability and lifespan |
| Investment Cost | Lower, suitable for small projects | Higher but long-term efficiency |
| Load Capacity | Limited power capacity, suitable for small loads | High load bearing, stable in industrial environments |
Detailed Analysis from Practical Experience:
In practice, residential electrical wires such as flexible single wires and flexible flat wires are often preferred for households and small offices due to their flexibility and reasonable cost.
Conversely, power cables and control cables are mandatory choices for large-scale industrial projects. This is precisely why Ngoc Lan Cable heavily invests in professional cable production lines to meet the diverse market demands.
Some cables are specially designed for specific applications:
- Underground cables: Have waterproofing capability and earth pressure resistance
- Fire-resistant cables: Use special materials to maintain operation in emergency conditions
Economic and Technical Efficiency Analysis: The structural differences lead to clear advantages and disadvantages
- Electric wires: Simple structure helps save costs but requires additional protection during installation
- Electric cables: Higher price but provides superior safety and lifespan, particularly important for critical electrical systems
Based on this general comparison, we will delve into frequently asked questions to further clarify specific selection situations.
3. Frequently asked questions about electrical wires and electrical cables
Based on our experience consulting with customers, we have compiled the most frequently asked questions along with professional answers.
3.1. Should I use electrical wire or electrical cable for indoor electrical systems?
Basic selection principles:
- Using electrical wire for lighting circuits, outlets, and household appliances (16A and below) is the appropriate choice in terms of both technical and economic aspects.
- Choose electrical cable for large industrial construction projects or underground burial to ensure long-term safety and durability.
Decision-making criteria for selection:
- Power capacity of equipment used
- Environmental conditions for installation
- Requirements for durability and safety
- Project budget
3.2. Why can electrical cables be buried underground while electrical wires cannot?
Different technical characteristics:
- Electrical cables: have protective sheaths that are waterproof, heat-resistant, and earth pressure-resistant according to IEC 60502 standard.
- Electrical wires: only have 1 insulation layer, easily damaged when exposed to high humidity and have no ability to resist mechanical pressure.
3.3. What is XLPE on electrical cables and what are its functions?
Definition and properties:
XLPE (Cross-linked Polyethylene) is a premium insulation material developed to replace PVC in high-requirement applications.
Superior advantages:
- Better heat resistance than PVC (90°C)
- 30-50% longer lifespan compared to PVC
- Oxidation resistance and crack resistance due to temperature
- Stable dielectric properties in harsh environments
Practical applications: In manufacturing plants, cables with XLPE sheaths demonstrate high stability in high-temperature environments and require less maintenance compared to cables with PVC sheaths.
3.4. How to correctly select the cross-section of electrical wires and cables?
Basic calculation steps:
- Steep 1: Determine the load current
- Steep 2: Calculate the wire length
- Steep 3: Check allowable voltage drop
- Steep 4: Select appropriate cross-section from standard reference tables
Factors to consider:
- Derating factors such as temperature derating factor, grouping factor, soil thermal resistivity, burial depth derating factor
- Installation method (in conduit, on cable tray, buried underground)
- Insulation material
- Electrical cable length
These questions reflect customers' actual needs and demonstrate the importance of clearly understanding the characteristics of each product type.
4. Conclusion
Through this article, you have clearly understood the differences between electrical wires and electrical cables, from structure and applications to technical standards. Choosing the right type of wire is a key factor in ensuring safety and efficiency for electrical systems.
Core differences:
- Protective structure – from simple to complex multi-layer
- Application scope – from residential to industrial
- Voltage rating and technical durability
- Compliance with TCVN and IEC standards
Clearly understanding these differences will help you make accurate decisions, optimizing both technical and economic efficiency for your project.
Contact Ngoc Lan Cable – a reputable supplier today to receive consultation and the best quotation for electrical wires and cables for your project. Our team of experts is always ready to support you in choosing the optimal solution.
 VN
VN