Have you ever encountered a situation where electrical devices suddenly stop working or even catch fire? Improper installation, overloading during use, or being affected by environmental factors can easily cause electrical cables to malfunction. So how can you recognize the common problems when using electrical cables and how to fix them? The article below will share with you some useful experiences on this issue.
1. The importance of understanding electrical cable faults
Do you wonder why understanding electrical cable faults is so important? Imagine a production run having to stop abruptly due to a power cable break, or a public lighting system collapsing due to a wire fire. Not to mention the risk of fire, electric shock and large property losses if not detected and handled promptly. Therefore, understanding the types of cable faults as well as how to prevent them is extremely necessary, not only for technical experts but also for ordinary users.
2. Common problems when using electrical cables
Cable faults stem from many different causes, which can be divided into main groups: Design & installation issues, operational issues and external environmental impacts. Here is a summary of common faults as well as signs to identify them for timely handling:
2.1 Issues related to design and installation
One of the most common mistakes when installing cables is choosing the wrong cable cross-section compared to the load requirements. If the wire is too small, the resistance will increase significantly when the load is high, causing overheating and even cable fires. Conversely, using oversized wires is wasteful and incurs high initial investment costs. So how to accurately calculate the required wire cross-section? First, you need to determine the rated current and short-term overload current (if any). Then, based on the rated current table for conductors provided by the manufacturer, choose the type of wire with a suitable current density.
Installing cables in harsh environments also easily leads to long-term faults. For example, places with high humidity, too hot or too cold temperatures all negatively affect the insulation sheath and cable life. Therefore, you need to pay attention to the environmental condition requirements to choose the appropriate conductors.
2.2 Operational issues
When put into operation, cables are likely to overheat if the load current exceeds the rated current for a long time. At this time, you may observe signs such as abnormally hot wires, even a burning smell from the electrical cable sheath. If there are no timely cooling measures such as reducing the load or increasing ventilation, the risk of short circuit and cable damage will be very high.
In addition, during use, electrical cables are also subject to mechanical impacts leading to damage. Strong collisions, excessive bending during installation or by other works on or near the cable route cause cables to be directly affected by external forces, causing damage. Therefore, when installing, it is necessary to have shielding and protection measures to avoid direct impacts and periodically check to quickly detect and repair damage.
2.3 Chemical and environmental issues
Under the impact of oxygen and high temperatures, the contact point between the cable and electrical equipment is easily oxidized, creating a thin layer of oxide that increases the contact resistance. The consequence is the generation of heat and electric arcs at that position. To avoid this phenomenon, you need to use anti-oxidation materials such as silicone glue to seal the joint, ensuring good contact.
High humidity conditions are also the cause of electrical cable faults. Just a small drop of water infiltrating through the sheath and getting inside the cable fiber can also cause the insulation to become moldy over time. Water acts as an electrolyte solution, creating conditions for leakage currents to run through the cable causing energy losses, and even causing fire if the voltage is high.
To prevent this, in addition to using waterproof cable sheath, you also need to carefully shield the terminals, avoid wet places and especially choose the type of cable that must be suitable for the installation environment.
3. How to fix problems when using electrical cables
When encountering problems related to electrical cables, depending on the severity of the issue, you can fix it in the following ways:
3.1 Replacing with new wires
For severe damage such as burning or broken wires that cannot be repaired, replacing with new wires is mandatory. When disassembling and installing, you need to pay attention to:
- Disconnect the entire power supply to the electrical wire system that needs to be replaced to ensure safety.
- Remember or take a picture of the wiring before disconnecting to avoid confusion.
- Choose the right type and cross-section of cable equivalent to or larger than the load capacity.
- Tightly and carefully connect the terminals to avoid poor contact.
- Tie the wires neatly, do not let them overlap in a messy and dangerous manner.
3.2 Temporary repair
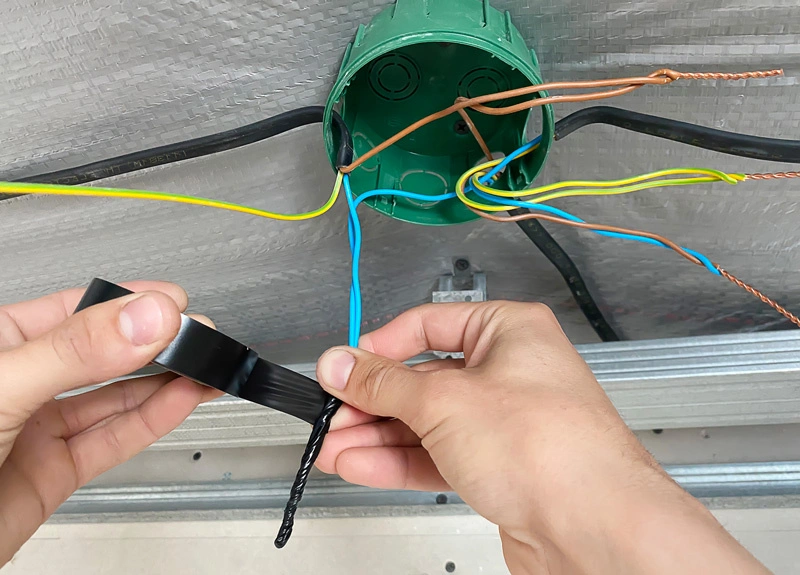
For minor damage such as scratches on the insulation layer, you can handle it by wrapping electrical tape or using heat shrink tubing. However, this is only a temporary solution; in the long run, you should still plan to replace with new wires for safety.
In addition, you absolutely must not use cable sections that have signs of burning or exposed copper strands to avoid the risk of short circuit and unfortunate accidents.
3.3 Technological solutions
In addition to the above manual remedies, applying technology to monitor cable conditions is also an increasingly popular trend. A thermal sensor system, for example, can help us quickly detect abnormal hot spots on power lines, avoiding dangerous incidents.
Short circuit and fire warning mechanisms are also integrated into protective switching devices, helping to isolate the faulty wire section from the rest of the electrical system, preventing widespread fires. You should research and invest in installing these smart technology solutions for proactive fault prevention.
4. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
4.1 What is the most common cable fault in coastal areas?
With the high salt content in the coastal air environment, contact oxidation occurs much faster than on land. In addition, cable dampness and mold are also frequent, leading to leakage currents and power loss. Therefore, when installing in coastal areas, you need to choose cables with good waterproof rubber sheath; if it is a bare conductor, choose one with a neutral grease layer on the outside to prevent corrosion. Pay special attention to insulating contacts with anti-corrosion glue or protecting the outer insulation layer.
4.2 Why do electrical wires get hot during use?
Electrical cables getting hot often stems from main causes such as overloading, poor connections, environment, and short circuits. Among them, poor connections are often the most common cause of electrical cable heating.
In addition to the basic root causes, electrical cables can still become overheated even when operating within the allowed current rating due to the following environmental factors:
- Ambient temperature higher than design standards
- High soil thermal resistivity reduces heat dissipation (for underground cables)
- Cable burial depth too large, limiting heat dissipation
- Location near other power lines causing thermal resonance
- Areas with many concentrated electrical circuits
- Installed near heat sources such as hot steam pipes
- Exposure to direct sunlight increases the temperature by about 10°C
4.3 What causes electrical short circuits?
A short circuit is the contact between two electrical conductors supplying the circuit, causing the wire resistance to suddenly increase, leading to electric arcing and causing fire and explosion. Common causes of short circuits include:
- Short circuit due to phase wires contacting each other or the live wire grounding, reducing the resistance leading to a sudden increase in current intensity causing overheating.
- The insulation layer of the wire is destroyed due to mechanical impact, high temperature or aging over time, causing the inner copper cores to come into contact with each other, creating an electric arc phenomenon.
- Animals like mice gnawing and breaking wires, causing the two poles to contact and close the circuit.
- Power source overloaded when using many high-power devices at the same time with high frequency.
5. Conclusion
So, we have gone through the common problems when using electrical cables as well as how to fix them accordingly. Although simple, this is all very useful knowledge, especially for newcomers such as electricians, engineering students as well as ordinary users.
In addition to proper installation and maintenance of cables, the most important thing is to choose quality cables that are suitable for the job right from the start to minimize problems later on. Don't buy low-quality products for cheap, instead, invest once in standard cables with good insulation, scratch-resistant and moisture-proof sheath to operate stably and safely for a long time.
In summary, equipping yourself with knowledge about electrical cables, as well as regularly checking and maintaining them is very important to ensure safety and operating quality for all electrical systems. Hopefully, through this article, you have gained more useful skills to work more effectively in the electrical industry.
 VN
VN